What Is the Polygon Bridge? A Step-By-Step Guide to Bridging.
Many projects are facing the issue of compatibility via developing bridges among networks. The bridges’ core function is connecting different blockchains to provide better flexibility for asset transfers. In this article, we will discuss the Polygon Bridge and give step-by-step instructions on how to bridge your assets with Polygon.
Key Takeaways
- Polygon is a side chain scaling solution that runs alongside the ETH blockchain.
- Polygon uses the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm.
- Polygon is a framework that helps create blockchain networks compatible with ETH.
- The PoS or Plasma bridges can transfer tokens to the Polygon network.
What is Polygon
Polygon is a network of secure Layer 2 (L2) solutions and independent side chains. It aims to increase the ETH blockchain’s scalability and reduce transaction costs.
The platform’s test network was launched in October 2017 under the name Matic Network.
The Polygon team created the Plasma Chains scaling model and Ethereum Matic PoS Chain side chain based on Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm. Over time, this side chain has become a popular scaling option for various applications.
Polygon offers an extension of the Ethereum infrastructure to solve the scaling problem. The platform provides algorithms that increase throughput and reduce the cost of transfers.
The Polygon architecture comprises four levels:
1. The Ethereum level ensures the security of the Polygon blockchains using smart contracts on the main network. This enables users to stake, resolve disputes and exchange information with the core blockchain.
2. The security level is required to access validators. The technology ensures the connection to nodes, interaction with them and distribution of rewards.
3. The Polygon level is represented by several independent blockchains. These blockchains ensure the creation of hierarchical connections between transactions and consensus. This level is used for transfers between users’ wallets.
4. The execution level is used for managing transactions and storing data. At this level, smart contracts are executed through networks compatible with Ethereum Virtual Machine (or EVM).
Thus, Polygon ensures the creation of autonomous and secure blockchains. Secure networks use the ETH infrastructure to provide a high level of security and privacy.
The ecosystem includes the EVM-compatible Matic side chain that operates on a PoS algorithm. The side chain algorithm allows the withdrawal of funds in staking from circulation, which provides additional protection.
The side chain is implemented at two levels: block production and validators. The validator level ensures the operation of the nodes, rewards payment, and the withdrawal of cryptocurrency from staking. This algorithm enables the implementation of side chain blocks into Ethereum.
The Polygon ecosystem includes over 7,000 DeFi apps, Gaming, and NFT. Polygon’s architecture offers developers a wide range of solutions that can be used for various application scenarios.
Polygon allows you to create applications focused on fast transactions. These applications use a blockchain with reduced time of block creation. The platform enables applications to interact at different levels and move between them.
The advantage of Polygon-based networks is EVM compatibility. The project is built based on ETH, which allows you to use its resources.
What Is The Polygon Bridge
Polygon is a framework that helps create blockchain networks compatible with Ethereum. Polygon’s objective is to enrich the ETH ecosystem utilizing tools that facilitate the creation of scalable decentralized applications (dApps). Popular DeFi platforms such as Aave, SushiSwap, and Curve are already deployed on Polygon.
To start interacting with DApps, all your assets stored on the Ethereum blockchain should be transferred to Polygon. For this purpose, the Polygon Bridge was developed.
The Polygon Bridge is a cross-chain bridge that facilitates transactions between the Ethereum and Polygon networks. With the Polygon Bridge, ETH users can transfer ERC tokens and NFTs (non-fungible tokens) to the Polygon network by means of smart contracts. With the Polygon Bridge, users can access dApps on the Polygon ecosystem.
How Does The Polygon Bridge Work
A dual consensus architecture ensures the transaction speed and decentralized nature of Polygon Bridge.
The Bridge also supports arbitrary state changes on side chains compatible with the EVM. Moreover, the Bridge can facilitate cross-chain token transfers immediately without any third-party restrictions.
When transferring through Polygon Bridge, the number of tokens in circulation does not change. When leaving the Ethereum network, the specified number of tokens are locked, and the same number of tokens are created in the Polygon network.
When transferring back to Ethereum, the supported tokens on the Polygon network are burned, and the tokens on the Ethereum blockchain are activated again.
The Polygon Network operates on two types of bridges to help transfer assets between the networks. These two types of bridges are the PoS Bridge and the Plasma Bridge.
The PoS Bridge is based on the PoS consensus algorithm. This algorithm helps to decide which user or users validate new blocks of transactions, ensuring the network’s security. Transfers to the PoS Bridge are made almost instantly; however, withdrawals can take some time to be confirmed. The PoS Bridge supports Ether (ETH) transfers and most ERC-based tokens.
Plasma Bridge supports transfers of the native token — Polygon MATIC — as well as the following tokens:
ERC-20 — a set of rules for creating ETH tokens.
ERC1155 — a multi-token standard that allows the creation of fungible, non-fungible, and semi-fungible tokens all in one contract.
ERC721 — a standard for non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
The significant difference between the Plasma and PoS Bridges is the withdrawal speed back to the Ethereum main net.
Due to the peculiar exit mechanism of the Plasma Bridge, withdrawals can take up to seven days. That is why users prefer the PoS chain for sending tokens back to the Ethereum mainnet.
However, interactions between Polygon and ETH are generally straightforward and relatively fast on both PoS and Plasma bridges, so you can choose whichever bridge complies with your needs and the tokens you want to transfer.
The Benefits Of Using The Polygon Bridge
Beside the network compatibility, using the Polygon Bridge has many benefits that can be unobvious, but still are very important for the future of the blockchains.
- Reduced transaction time. Unlike the traditional financial systems, the Polygon Bridge can complete transactions in seconds or minutes due to the decentralized nature of the network. Since the Bridge uses advanced algorithms, transactions are completed faster and with improved efficiency. This fact makes the Polygon Bridge a good option for those who want to transfer digital assets quickly.
- Security. Thanks to the decentralized nature and advanced encryption methods, the Polygon Bridge ensures high security of your transactions. Moreover, it makes it impossible for hackers to compromise the network and steal your digital assets.
- Low transaction fees. Thanks to its decentralized nature, the Polygon Bridge can offer lower fees that are calculated accurately and fairly due to the advanced algorithms.
- Transparency. Every transaction in the network is recorded on the blockchain, which means it is visible to everyone on the network. The ability to trace every transaction to its source eliminates the possibility of frauds and adds to the security.
- Future Potential. As the use of cryptocurrencies continues to evolve, crypto bridges are likely to become even more important. The Polygon Bridge provides a high level of security and reliability for transferring crypto assets across blockchain networks, which is becoming increasingly important with the continuous growth of cryptocurrency transfers.
How To Use The Polygon Bridge
Transferring tokens to the Polygon network using bridges is called bridging. Both Plasma Bridge and PoS Bridge can be used for this purpose. However, most users prefer PoS Bridge since it is more convenient and compatible with many ERC tokens.
To start bridging, you must place your assets in a compatible crypto wallet and then log in to the Polygon Bridge area to access various tokens.
Currently, the Polygon Bridge supports a lot of wallets, for example, such as Coinbase Wallet, Venly, Metamask, Bitski, and some other wallets compatible with WalletConnect.
Metamask is considered one of the most popular Web3 wallets, and many users prefer this wallet.
We will use Metamask as an instance wallet to guide you through the process of utilizing the Polygon Bridge.
You have to add the Polygon Mainnet to the MetaMask wallet in order to start using Metamask with Polygon. To do this, proceed with the following steps.
1. Go to the Polygon Bridge Web Wallet and click Connect to Wallet.
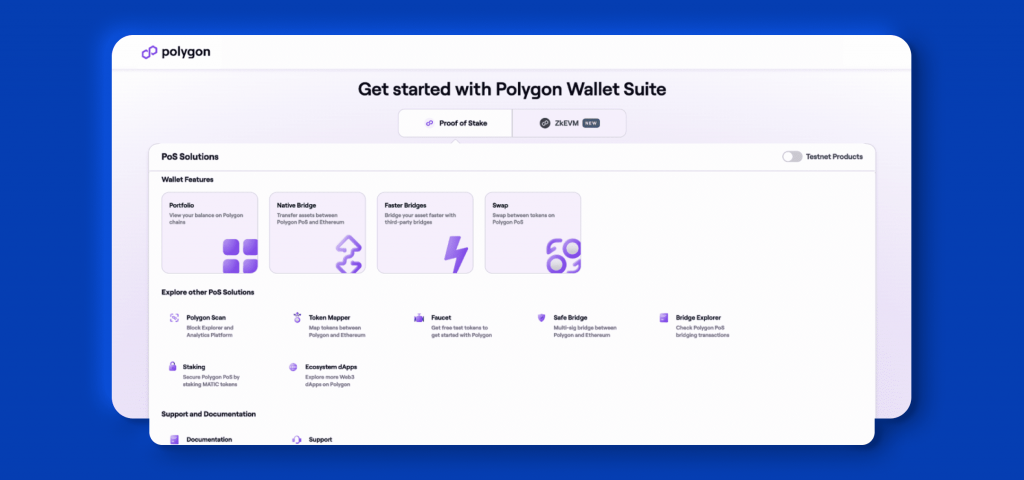
2. Select the MetaMask wallet (or another wallet that you prefer).

3. Open the MetaMask wallet on your smartphone and click the scan icon located at the top of the screen.
4. Scan the QR code on the Polygon Web Wallet page.
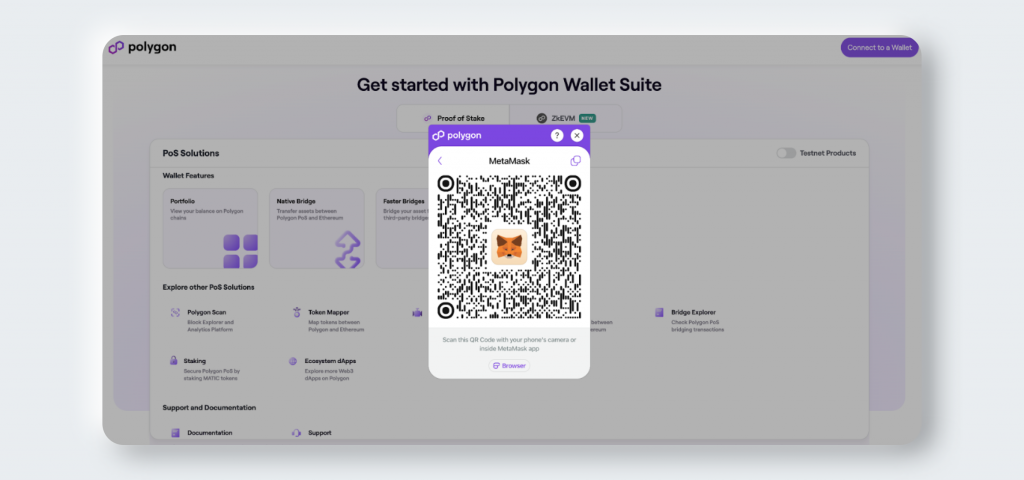
5. On your MetaMask wallet, click Connect.
6. As soon as the connection is established, a confirmation pop-up window on your app appears and you are redirected to the Polygon Bridge page. If not, click Bridge in the left menu bar.
Now you can send tokens from the ETH network to the Polygon blockchain. The platform automatically selects the bridge (PoS or Plasma) depending on the token type; however, you can change the bridge to the one of your choice. Before transferring, make sure there are enough tokens in your wallet and then perform the following steps.
1. Select the token, enter the token amount, and click Transfer.
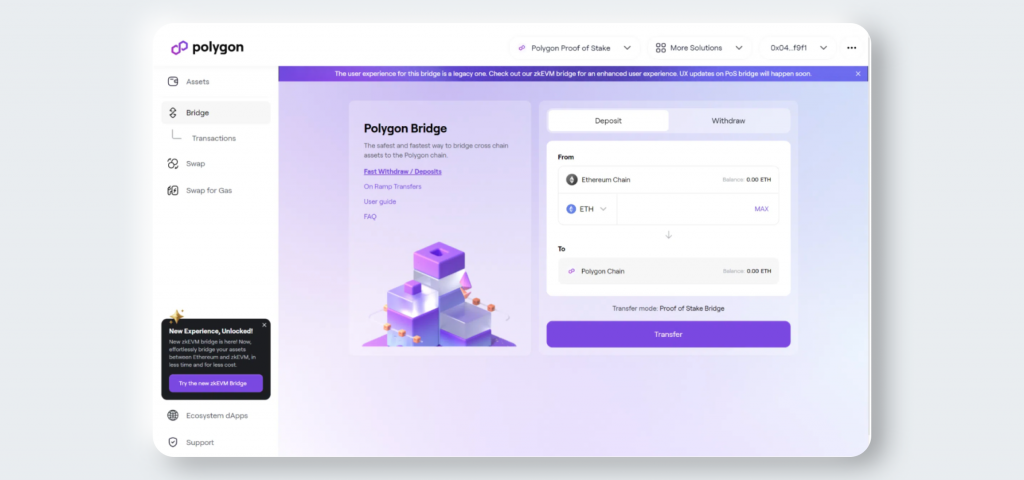
2. Carefully read the important information in the pop-up regarding the token transfer and click Continue.
3. Confirm the amount of tokens to bridge, gas fees and operational costs and click Continue.
4. Approve the transaction in your wallet. Then, check your MetaMask wallet, confirm the details there and click Confirm. Note that bridge transactions to and from Polygon cannot be reversed.
After you confirm the transfer, the tokens will appear in your Polygon wallet. The transfer might take some time, from a few seconds to a couple of minutes, depending on how busy the network is.
You can view the transaction status on Polygon scan by clicking the corresponding button on your MetaMask wallet.
You can manage the tokens on Polygon at your discretion. For example, you can interact with dApps, buy and sell NFTs, or swap one token for another using DEX Apps.
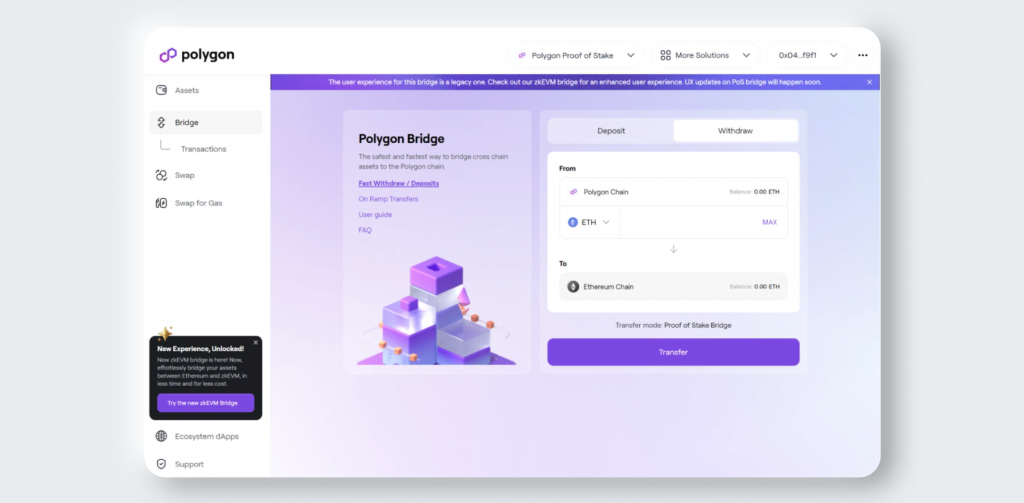
To withdraw Polygon tokens from ETH, move to the Withdraw tab. The blockchains will automatically switch places, and you can proceed with the transfer.
Conclusion
The Polygon Bridge is essential for the future of the crypto world since it can ensure better compatibility between blockchain networks. It can also be used to transfer NFTs within the crypto ecosystem.
Moreover, the PoS and Plasma bridges on Polygon Network can be good options for those who want to explore DeFi platforms and dApps associated with Polygon.
FAQs
What is the benefit of the crypto bridge?
The key advantages of crypto bridges are reduced transaction time, enhanced security and transparency of crypto operations, lower transaction fees, and the global nature of the bridges that ensures that they are not limited to specific geographic regions like traditional financial systems.
What is the difference between the Plasma Bridge and the PoS Bridge?
Both Plasma Bridge and PoS Bridge are MATIC bridges. However, they use different security techniques. The PoS Bridge uses a PoS mechanism and relies on external validators, while the Plasma bridge relies on the security system of the ETH blockchain.
Can I transfer BNB tokens to Polygon with the Bridge?
Yes. It is possible to transfer BNB tokens to Polygon via the PoS Bridge. To bridge BEP-20 to Polygon, you have to exchange BEP-20 for ERC-20 and then swap the tokens. The swapping procedure is necessary since BEP-20 tokens are similar to the ERC-20 tokens, however, they are based on different blockchains.



