A Brief Introduction To The Graph
Building a decentralized application (or dApp) on the Ethereum blockchain can be challenging. Though the concept of blockchain is similar to that of databases, storing data on blockchains can cause significant performance issues connected with their decentralized nature and the variety of consensus protocols. Some of these issues can be solved by implementing decentralized protocols. In this article, we will discuss a decentralized protocol for indexing and querying blockchain data, and learn what The Graph is and how it works.
Key Takeaways
- The Graph is a decentralized protocol designed to index and query data from public blockchain networks.
- Data indexation is performed via subgraphs that are essential functional elements of The Graph created by third-party developers.
- GRT is the native token of The Graph that is essential for the proper operation of the system.
What Is The Graph
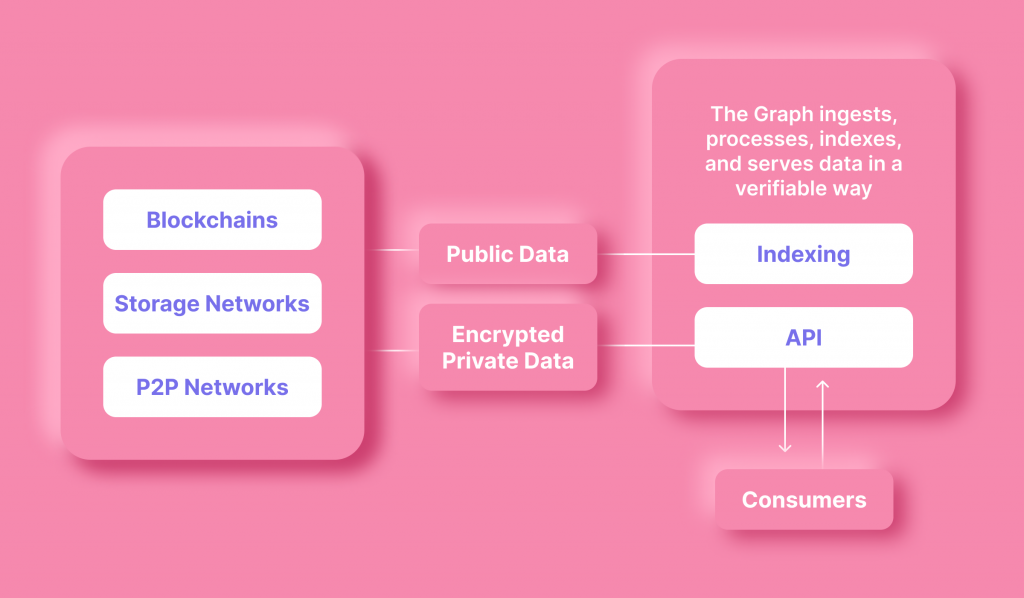
The Graph is a decentralized open-source protocol for indexing and querying data in the blockchain. The Graph protocol can collect and store data from other blockchains; it is powered by blockchain technology and is hosted on the Ethereum blockchain, ensuring transparent and secure transactions.
The users can create and publish open APIs that enable the users to access data that are difficult to get directly from the blockchain. These APIs are called subgraphs.
The deployed subgraphs are stored in The Graph Explorer. The explorer is also used for accessing data and selling GRT on cryptocurrency exchanges.
The subgraphs are transferable, allowing developers to use GraphQL (the language used by The Graph) to query data quickly and efficiently.
With the help of The Graph’s advanced interface, developers can access data collected on decentralized networks and thus speed up the creation of decentralized applications on those networks.
The Graph protocol currently supports many leading DeFi protocols, including Synthetix, Uniswap, Aave, Balancer, Aragon, etc.
These DeFi protocols query data such as trading operations, DEXs liquidity, and so on, from the subgraphs, which makes The Graph a crucial component for providing security and transparency for DeFi apps.
The main difference between The Graph and similar existing blockchains, like, for example, Etherscan, is that The Graph protocol aims to provide a truly decentralized solution. Another key difference is that The Graph’s technology will enable dApps to access all kinds of blockchain data and not be limited to the information provided by a particular data provider.
Today, The Graph provides indexation for such blockchains as Ethereum, Polygon, Arbitrum, BSC, Celo, Avalanche, XDAI, POA, and Fantom.
The unique feature of The Graph blockchain derives from its purpose: to provide an easy access to data for consumers on The Graph network. The Graph is the first decentralized marketplace that tackles the difficulties associated with creating dApps in terms of resolving indexing issues and proprietary concerns.
The value of The Graph is defined by total and circulating supply and its blockchain architecture. Also, The Graph has its technical and market value as GRT tokens are traded in the cryptocurrency market.
The History Of The Graph
The Graph was founded in 2018, driven by the idea of simplifying the creation of dApps of Ethereum. The Graph was launched by Yaniv Tal, Brandon Ramirez, and Jannis Pohlmann as the first decentralized indexing and querying app on the market.
One of the core aspects of The Graph’s design was its open-source code based on GraphQL — a language for API requests and a framework for executing source files with existing data.
In October 2020, before the launch of The Graph’s main network, the project team distributed its native cryptocurrency — GRT tokens — among potential network participants. The initial supply of circulating tokens was set at 1,245,666,867 GRT tokens, 400 million of which were sold for $0.03 in ETH each. After three years of beta testing, The Graph’s main net went live in December 2020; during this time, about 12.5% of the token total supply went into circulation.
Shortly after its launch, The Graph received many high-level integrations from emerging DeFi platforms. The network indexes data from Ethereum, InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), POA, and other networks.
How Does The Graph Work
The Graph works as a protocol that indexes and organizes data from blockchains and processes it into a more accessible form. With this protocol, developers can create subgraphs, or public APIs, that allow decentralized applications to search and process information from the blockchain.
The Graph can index data in blockchain similarly to Google indexes web pages. During this process, files, data, and metadata are searched and cataloged so that results can be quickly found.
To aggregate data, The Graph Nodes continuously scan network blocks and smart contracts for information.
When an application adds data to the blockchain through a smart contract, the Graph Node adds the data from these new blocks to its appropriate subgraphs.
For example, the Uniswap website gets data for charting, coin rates, etc., from Uniswap smart contracts that are deployed on the Ethereum network. These data are taken from The Graph network through GraphQL queries.
In simple words, The Graph removes the need to store and constantly update data on the websites’ servers, since new blocks, transactions, and other events are permanently present on the Ethereum network. The Graph nodes constantly scan the network and update the subgraphs that store this data.
Updating data via a browser can be time consuming, while storing data on servers can be expensive. The Graph is designed to reduce the cost and simplify the process of obtaining information from the Ethereum blockchain.
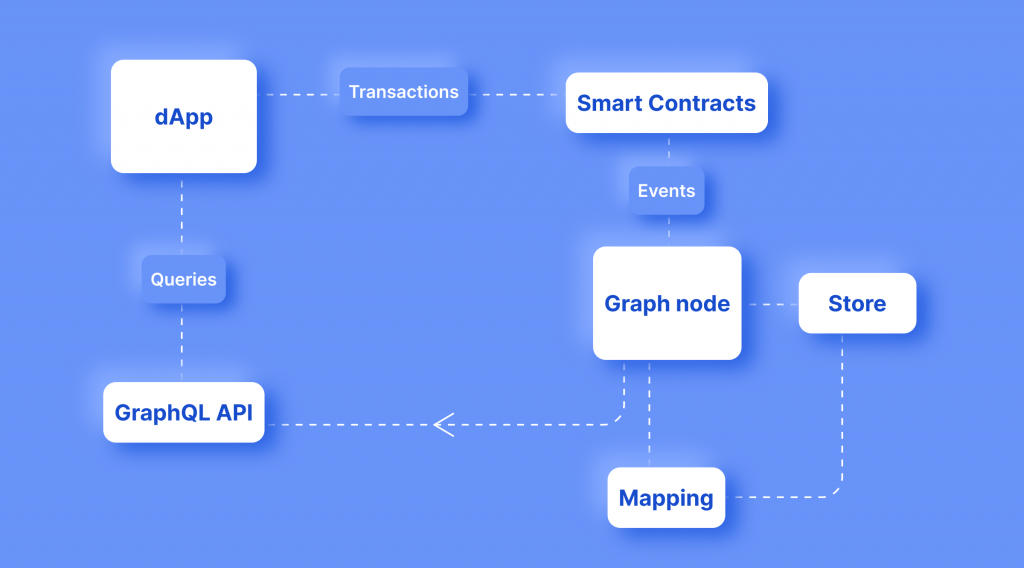
The Graph Network follows the principles of maximum decentralization: most of the protocol’s stages are distributed among thousands of community members, who receive the GRT tokens as revenue for their contribution to the operation of the network.
The Graph uses a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, which involves staking for network members. Once The Graph Node extracts information, four groups of network participants contribute to organizing data in its protocol.
- Indexers. They are node operators who index the blockchain and process requests in exchange for a reward. However, if the node provides incorrect data, the operator is penalized.
- Curators. These community participants assess the subgraphs and send signals to indexers about the ones of superb quality, that is, the subgraphs that contain valuable data and should be indexed. A signal is generated when a curator places their GRTs in a specific subgraph. Moreover, if several curators vote for a subgraph, they will all receive a part of the request commission in proportion to their contribution.
- Delegators. These members can delegate tokens to one or more indexers, receiving a share of the request processing rewards. However, if the delegator decides to revoke the GRT, they must wait 28 days for it to be unlocked.
- Consumers. These are the end users of the protocol, who use the GraphQL language to get data from the subgraphs. Consumers pay GRT tokens to use The Graph’s services and benefit from the services the network provides.
Indexers can run their own The Graph Node for any EVM-compatible blockchain. Nodes also can interact with other blockchains through integration with the Firehose tool. Such networks as NEAR, Arweave, Solana, and Cosmos are accessible via The Graph Node.
The Graph enables developers to create Web3 applications that do not need centralized servers; such applications can run entirely on a public, decentralized infrastructure.
What Is The GRT Token?
GRT is a native token of The Graph. The token is essential for the entire system’s operation: the indexing process cannot be started without the token since the service fees are charged in these coins. That is, to make a query to The Graph, a user has to pay with the GRT token.
GRT is the primary token of the indexing protocol that is used to query the Ethereum or IPFS networks.
The GRT is an ERC-20 token, which implies that it is built on Ethereum and can be stored in any wallet with the ERC-20 token support.
GRT was first put up for sale at the end of 2020. After this, the capitalization of the coin reached 1 billion USD in 3 days.
As of 2023, The Graph (GRT) has 4.72B GRT in circulation, and the total circulation of the token is 10,000,000,000.
How To Mine GRT?
GRT cannot be mined as Ethereum or Bitcoin because The Graph is based on the Proof of Stake consensus. Instead, users can earn tokens being the participants of The Graph network in the role of indexers, curators, delegators, or consumers.
Some CEXs also offer staking rewards for users who lock up their GRT tokens for a specified period.
Pros And Cons Of The Graph And GRT
Being the pioneer in indexing, The Graph offers its users many advantages, such as an open community and an independent technical governing body that supports the monetary policy of GRT.
Among the drawbacks of The Graph, experts point out its centralized nature since, for now, the project remains centralized.
The Graph’s token, GRT, also has its pros and cons. Among the benefits of the token are the following:
- Connection of dApps with blockchain data. The role of The Graph is to simplify complex data processing and provide consumers with the data they request.
- Smart contracts. One of The Graph protocol’s main advantages is smart contracts that provide security and transparency for all processed data.
- Successful public sale. The Graph managed to raise over $12 million in public sales, showing the anticipation and excitement around the project.
- Accessibility. GRT can be purchased on most crypto investment platforms, such as Binance, Kraken, or Etoro.
- Decentralization. The GRT token is a virtual currency with decentralized network management.
- Fees and security. The Graph is considered a highly secure network with relatively low transaction fees.
Among the core disadvantages of the GRT token is its market capitalization, which is relatively low compared to other cryptocurrencies. Also, because GRT is a relatively new token in the market, it has not yet had time to prove its duration.
What Is The Future Of The Graph
The Graph protocol facilitates the data processing with the help of subgraphs, which are part of a much larger system.
Thanks to this fact, the project drew the interest of such companies as Uniswap.
However, the future success of The Graph depends on how many influential projects will be interested in The Graph’s services in the future. Considering this, The Graph Council has announced its intention to partner with more projects to provide blockchain data discovery and processing for these projects.
The future development of the project will also impact the GRT token. However, the analysts have different, sometimes even opposite, estimations of GRT’s future.
Thus, according to the PricePrediction.net forecast, the GRT could be worth $0.18 this year, $0.27 next year, and $0.39 the year after that, and by 2028 the token could break the dollar barrier and cost $1.14.
However, the assessment of The Graph’s token growth made by WalletInvestor is less optimistic. According to the site’s forecast, the GRT price could fall to $0.0157 in April 2024.
The true potential of The Graph project has yet to be revealed. Nevertheless, the indisputable fact is that the project is vital for the DeFi market since it can speed up and simplify the process of obtaining the necessary information. The networks are fragmented, and bridges must be created between them to ensure smooth data transfer. The Graph can be one of these bridges that can ensure advanced security, reliability, and transparency.
Conclusion
The Graph is one of the new Web3 projects, launched only in 2020. Many well-known blockchain platforms already approved the project. The Graph is a critical project for the DeFi market that can become a bridge between different networks and add to the security of transactions. However, the future of GRT is still being determined. Many experts predict an increase in its price in the next few years, while others believe that the value of GRT will fall. If you plan to invest in GRT, research and come to conclusions about where you think the prices are headed.
FAQs
Is The Graph (GRT) worth buying for investment?
GRT is a relatively new token in the market, so the opinions about its future profitability differ. Some experts claim that The Graph (GRT) is a good investment since its price will increase, while others say the token will lose its value.
What Does The Graph Do?
The Graph is a decentralized protocol that enables developers to index and query data from various blockchains (for example, Ethereum, POA, or IPFS). With this protocol, developers can build dApps to access relevant data without centralized intermediaries.
How can I buy The Graph token?
To buy GRT, select the exchange that sells the token (for example, Binance, Etoro, or Kraken) and create an account. Then you need to make a deposit using your credit or debit card or other payment means (for instance, you can buy GRT with Bitcoin). The last step is to use the deposited funds to buy GRT, following the instructions on the selected platform.



