Bitcoin vs Wrapped Bitcoin: How Do They Differ?
Bitcoin is the world’s largest and most widespread crypto asset. It suggests its holders numerous benefits, including high security and decentralization. However, the inability of BTC holders to use DeFi applications sparked the discussion about wrapped tokens, which ultimately led to the creation of WBTC. Despite having similar names, Bitcoin and Wrapped Bitcoin vary significantly in how they function inside the blockchain environment.
In this article, we will take a closer look at Wrapped BTC, its difference from Bitcoin, and discuss its benefits and issues.
Key Takeaways
- Wrapped tokens are crypto tokens supported by other original assets, like stocks, gold, or cryptocurrency.
- Wrapped BTC is a tokenized form of BTC that represents Bitcoin on the ETH blockchain.
- WBTC is pegged to BTC and works on both BTC and ETH networks.
- Third-party intervention when minting WBTC can be a problem for tokenized crypto.
What is a Wrapped Token?
Wrapped tokens are virtual currencies supported by the value of other original assets like gold, crypto assets, or stocks and put to work on the DeFi platforms.
The original asset is wrapped into a digital vault, and a newly minted token can be transacted on other platforms. Wrapped tokens build bridges between networks by enabling the use of external assets on any blockchain.
The idea behind the wrapped crypto is almost the same as that of stablecoins: the token’s value is backed up by the base crypto, meaning that 1 token equals 1 base crypto. This enables the use of tokens in different blockchains.
There is a wide range of wrapped cryptocurrencies in the market but wrapped bitcoin, or WBTC is the most commonly used.
What is Wrapped Bitcoin?
The high liquidity of Bitcoin made it the most popular crypto asset; almost everyone in the crypto world holds BTC. According to CoinMarketCap charts, Bitcoin is the largest cryptocurrency by total market capitalization.
However, the BTC protocol cannot keep up with new developments in decentralized finance and does not fulfill all the needs of current-day crypto businesses.
The Bitcoin protocol cannot be used to create and run the smart contracts used for the DeFi ecosystem along the Bitcoin blockchain.
Ethereum, on the other hand, has a solid smart contract ecosystem. Thus, the ETH network is a compatible basis for DeFi products (or DApps). As a matter of fact, Ethereum is the primary blockchain used for this purpose.
The main disadvantage of Ethereum’s blockchain is that only ETH-based assets, that is, only ERC-20 tokens, can operate on the network. This significantly limits the growth of the DeFi ecosystem.
Wrapped BTC is a bridge between Bitcoin and dApps that work on Ethereum and are so widespread in DeFi.
Being an ERC-20 token, WBTC operates on the Ethereum network and is supported by BTC (that means one WBTC equals one BTC).
Wrapped Bitcoin is an innovative technology that makes the Bitcoin and Ethereum networks compatible.
With the wrapped technology, the BTC holders got access to the DeFi ecosystem and all its functions that are not available on CEXs, such as, for example, staking. Moreover, smart contracts used on ETH increased Bitcoin transactions’ speed, security, and efficiency.
Different blockchains might be non-compatible since they work on different protocols. This is where wrapped tokens, such as Wrapped Bitcoin, come to assistance by allowing the transfer of liquid crypto assets between the blockchains.
In a few words, Wrapped Bitcoin is a Bitcoin that was turned into a token to be able to run on the ETH Blockchain.
WBTC — is an ERC-20 token that is one-to-one pegged to Bitcoin, meaning that 1 WBTC equals 1 BTC. The main difference between WBTC and BTC is that Wrapped BTC can be used on the Ethereum blockchain and in Ethereum-based dApps.
Before WBTC, Bitcoin was used in financial transfers only through CEXs.
WBTC’s launch in January 2019 aimed to provide access to Bitcoin for dApps on Ethereum.
WBTC is routinely swapped on DEXs and used as collateral on lending and derivatives platforms.
How Does WBTC Work?
WBTC works through a wrapped technology, transferring cryptocurrency between blockchains by creating the tokenized version of the crypto asset and keeping the asset value.
Besides the user, three critical actors in the WBTC managing process are merchants, DAO, and custodians.
- DAO is the regulatory body. It comprises 17 stakeholders and over 40 members, including merchants, exchanges, wallets, and more.
- Custodians are responsible for minting and unwrapping WBTC tokens; they also guarantee the safety of the BTC reserves.
- Merchants act as WBTC distributors. They notify the custodian to wrap and unwrap Bitcoins and deliver the wrapped tokens to the end user.
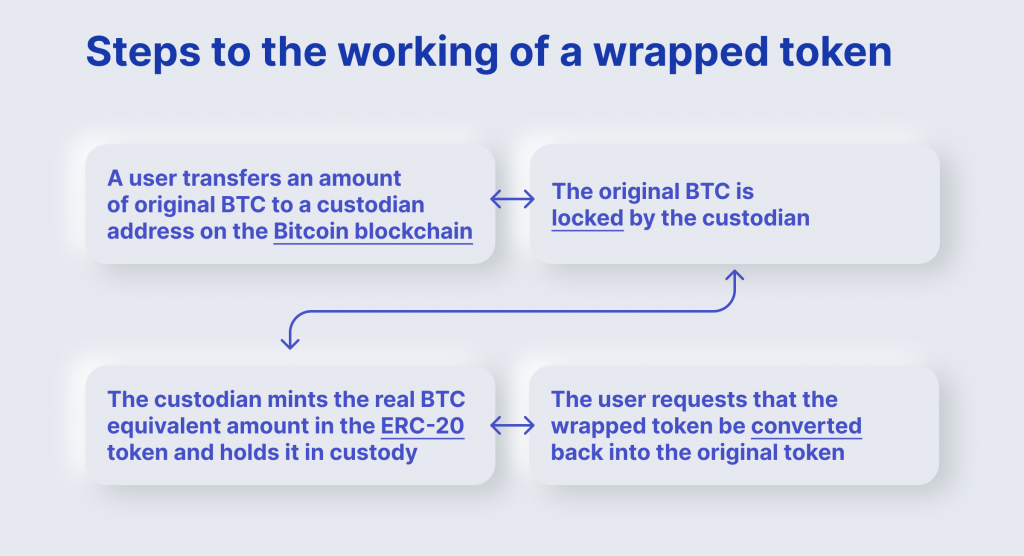
Custodians exchange assets for wrapped tokens with merchants via two transaction types; minting and burning.
Minting is the production of wrapped crypto tokens, whereas burning refers to reducing the supply of wrapped tokens. These transactions are available publicly and can be viewed by anyone through a block explorer.
How is WBTC Created?
WBTCs are derived from BTC, so to mint wrapped bitcoins, you must deposit BTC.
To buy Wrapped Bitcoin, a user has to implement several steps:
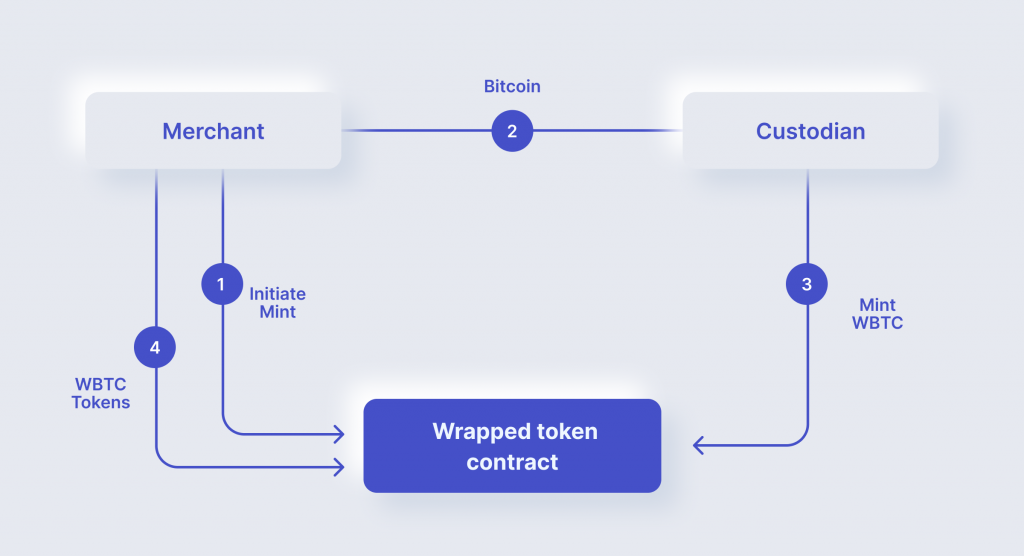
1. A user chooses a merchant to manage the transaction process and then submits a request for buying WBTC tokens.
2. The merchant conducts KYC/AML activities to prevent fraud and money laundering and submits the request to mint the specified amount of wBTC to a custodian.
3. The custodian blocks BTC in the custodian’s account, and the corresponding amount is minted in WBTC on Ethereum.
4. The user and the merchant enter a transaction on a CEX or DEX. As a result, the user takes the WBTC, and the seller receives BTC.
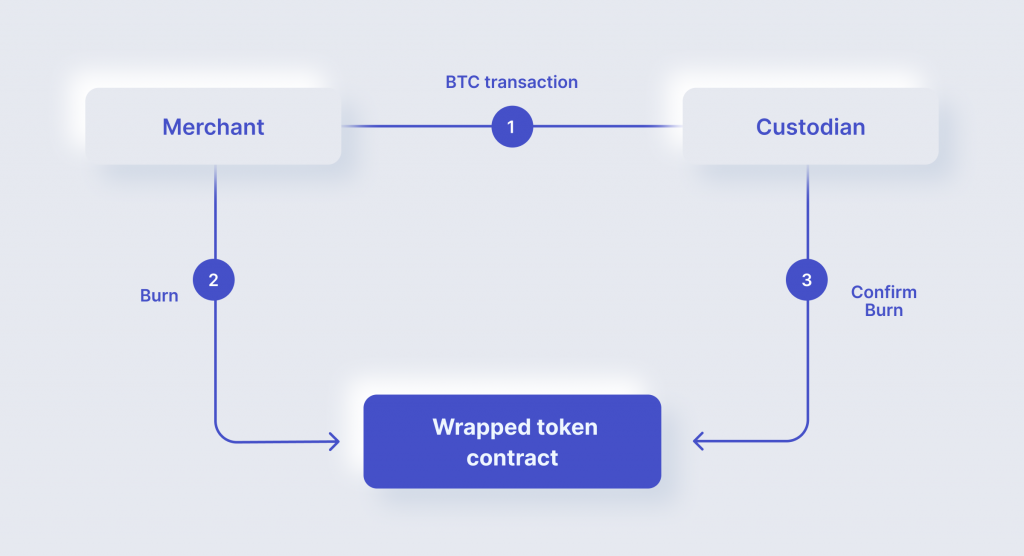
The user can also redeem BTC from WBTC tokens, that is, start the process of token burning. This process is similar to WBTC minting.
1. The user requests a specific amount of BTC from the merchant.
2. The merchant creates the burn transaction and sends the request to the custodial.
3. The custodial unwraps the specified amount of WBTC — burns the wrapped token — and provides BTC corresponding to the number of received tokens.
4. The user receives BTCs, and the merchant burns the wrapped tokens.
Fees
Transfers of WBTC between users are cost-free, though network fees are applied.
There are three ways in which different parties of the WBTC managing process can earn fees:
- Merchant fees – The merchant charges this fee with which the user exchanges wrapped tokens for the asset.
- Custodian fees – The custodian charges this fee when the merchant mints or burns wrapped tokens.
- Sidechain transaction fees – This fee is shared equally among all institutions running nodes on the sidechain. Such a fee is aimed at preventing spam on the sidechain.
Wrapped Bitcoin vs. Bitcoin
Though WBTC derives from Bitcoin, their use cases have a significant difference.
Bitcoin was created in 2009 and was intended to function as a peer-to-peer payment system. Over the course of time, the value of BTC increased, and Bitcoin holders can now use the cryptocurrency to buy goods, pay for services, invest in it or even use it as a viable store of value and a hedge against inflation.
Wrapped Bitcoin is a token version of Bitcoin that allows users to access DeFi apps, smart contract-driven platforms, and DEXs. WBTC can also draw liquidity to the Ethereum ecosystem from holders of BTC. WBTC holders can use smart contracts, deposit assets into DeFi protocols, and take out a loan to purchase even more WBTC.
Pros and Cons of WBTC
Being a tokenized Bitcoin, WBTC comes with many advantages for its holders. The core benefit of the crypto asset is that it can be used on the Ethereum blockchain, which allows the token holders to access DeFi. But there are other benefits of WBTC. Let’s take a closer look at some other advantages of Wrapped Bitcoin.
Liquidity
Wrapped Bitcoin is an effective tool that can increase liquidity both on DEX and CEX. Bitcoins are mainly used on CEXs, and ETH is typical for DEXs. At the same time, WBTC eliminates the necessity to exchange BTC for ETH, meaning that with WBTC, users can move their assets across the network without any obstacles.
Smart Contracts
WBTC enables BTC holders to use all the advantages of DeFi, including smart contracts. They remove third parties from the process of transaction executions, which leads to improved profitability and speed of transactions and makes them more secure.
Staking
This widespread DeFi function enables cryptocurrency holders to earn revenue from holding their assets in the dedicated pools where they are locked for remuneration. Bitcoin cannot be staked; however, its tokenized version can. Wrapped Bitcoin token staking allows BTC holders to benefit from staking WBTC and improve the efficiency of their assets. CoinList is one of the well-known platforms for WBTC staking.
Besides the advantages, WBTC brings some concerns to the crypto community. The substantial limitation of WBTC usage is its lack of privacy.
When minting WBTC, users have to trust their assets to a third party (a custodian), raising a question of asset security.
Wrapping cannot be automated through a smart contract on the Ethereum digital ledger. It is performed via a central program, therefore, open for potential manipulation.
Some experts claim that in the future, this could seriously undermine the idea of decentralization that underlies the whole blockchain industry, including Bitcoin and Ethereum.
How to Use WBTC?
The core idea of WBTC is to enable Bitcoin holders to use tokens from one platform on another platform.
Here are some ways that WBTC (as well as other wrapped currencies) can be used.
Speed Up Your Transactions
The ETH blockchain is faster than the Bitcoin one, so if you want to speed up your transactions, you can opt for WBTC since wrapped Bitcoin allows using your BTC reserves on the Ethereum platform.
Increase liquidity
Bitcoin is commonly used on CEXs, while Ethereum is prevalent on DEXs. With WBTC, exchanging BTC for ETH to go to a DEX is unnecessary because WBTC works on both networks.
Smart Contracts
Bitcoin is not used for smart contracts, but with WBTC, bitcoin can back transactions based on them.
Conclusion
The concept of wrapped assets allows the owners of previously non-compatible digital assets to profit from dApp and invest their assets via platforms they didn’t have access to. A combination of BTC liquidity and the technological advancements of ETH can make wrapped Bitcoin one of the most profitable cryptocurrencies. However, some drawbacks, like safety issues and lack of privacy, still need to be addressed.
FAQs
Is Wrapped Bitcoin better than Bitcoin?
The better option for you depends on your goals. If you are looking to keep a store of value, Bitcoin could be a good option. But if you want to make DeFi transactions or are interested in dApps, you can purchase WBTC.
Can WBTC become more valuable?
Wrapped BTC is backed by BTC, meaning the token’s price and value will increase and decrease along with Bitcoin’s.
Why do we need wrapped Bitcoin?
The primary purpose of WBTC is to enable traders to use their Bitcoin reserves on the ETH blockchain without exchanging BTC for ETH.
Is WBTC good for investment?
It depends on your objectives and portfolio strategy. WBTC is pegged to BTC, so if you think that WBTC will remain the main version of tokenized BTC and expect BTC’s price to rise, WBTC might be a reasonable investment.



