The Reality of Bitcoin Anonymity and Traceability
In recent years, cryptocurrencies have faced scrutiny and skepticism from governments around the globe, including in India, China, the US, and Europe. Once hailed as an untraceable underground currency, Bitcoin and other digital currencies have gradually revealed their vulnerabilities.
Notable incidents, such as the 2015 sentencing of the creator of the infamous ‘Silk Road’ Bitcoin market, highlight the ability of investigators to follow the money trail. Even cryptocurrencies designed for heightened privacy, like Monero, DASH, and Verge, are not entirely anonymous due to the transparent nature of blockchain technology.
With every transaction recorded and accessible on a public ledger, the question remains: Are Bitcoin transactions anonymous? Can individuals conduct transactions without revealing their identity?
Key Takeaways
- Cryptocurrency transactions involve transferring information between blockchain addresses validated by a network of nodes.
- Anonymity in the Bitcoin transaction is actually pseudonymity, with wallet addresses replacing real-world identities.
- Bitcoin transactions can be traced using blockchain explorers, linking activities to public keys but not revealing personal information.
- Tracing Bitcoin transactions can be made challenging through methods such as using mixers or creating multiple wallets.
- To maximize anonymity, avoid reusing addresses, use pseudonyms, and exercise caution with online wallets.
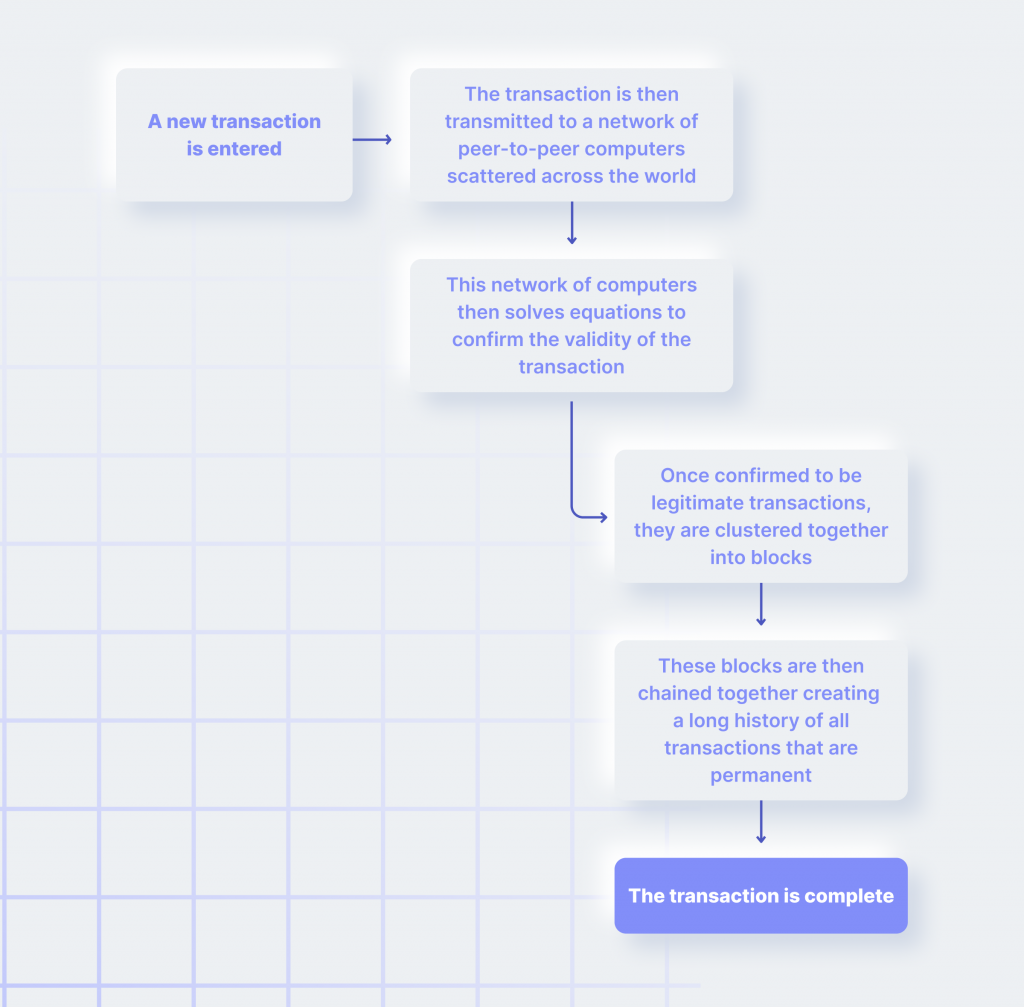
Crypto Transactions From A to Z
At their core, cryptocurrency transactions involve the transfer of information between blockchain addresses. To execute a transaction, it must be signed with a private key corresponding to the associated address.
Upon signing, the transaction is broadcast to a network of nodes — active computers that adhere to specific rules for validating transactions and blocks. For a transaction to be considered valid, it must be confirmed through inclusion in blocks via the mining process.
This infrastructure guarantees that transactions are transparent, and once they are deeply embedded in the blockchain, they cannot be altered or erased from the records. In contrast to traditional currencies, which are physical and regulated by the central authority, cryptocurrencies are entirely digital and decentralized.
As a result, transactions can take place directly between individuals, eliminating the need for intermediaries like banks or payment processors. This feature makes cryptocurrencies an attractive, expedient option for conducting transactions across the globe.
Are Bitcoin Transactions Anonymous?
Contrary to popular belief, Bitcoin does not offer true anonymity. On the blockchain, transactions are identifiable only through an alpha-numeric string known as a public key. This feature renders Bitcoin transactions pseudo-anonymous, meaning others can view your transactions and holdings, but they cannot discern the real-world identity associated with the public key.
However, this level of anonymity diminishes when you need to exchange your cryptocurrency for cash or other tokens or obtain a crypto debit card. You must register with a centralized crypto exchange, decentralized application, or crypto bank to access such services. These platforms typically require you to complete a Know Your Customer (KYC) process to become a client.
By complying with KYC requirements, you inadvertently establish a connection between real-world data and the public key of a wallet, which can then be exploited to unveil details about the identity behind the wallet’s public key.
In essence, while the Bitcoin transaction initially appears anonymous, engaging with various services within the cryptocurrency ecosystem can potentially compromise the anonymity users desire, linking their real-world identities to their digital transactions.
Is It Possible To Have An Anonymous Bitcoin Wallet?
While the notion of an anonymous Bitcoin wallet is enticing and theoretically achievable, it is essential to recognize that a Bitcoin wallet alone cannot guarantee absolute anonymity. As numerous transactions take place, an identity may eventually be linked to a wallet containing the relevant information.
Moreover, the widespread adoption of Know Your Customer (KYC) policies by most crypto exchanges has rendered the concept of conducting anonymous transactions increasingly impractical. Nevertheless, some crypto wallets enable users to transact with a degree of anonymity. For instance, the Electrum wallet can be integrated with a hardware wallet to facilitate more discreet transactions.
Considering how you want Bitcoin to be sent to you when using an anonymous wallet is crucial, as any Bitcoin transferred from an exchange with KYC requirements will render anonymity futile. Therefore, while anonymous Bitcoin wallets may be possible, their effectiveness is contingent on the context in which they are used.
Is It Safe To Publicly Share Your Bitcoin Wallet Address?
Sharing your Bitcoin public address is generally considered safe, as it enables others to send donations or payments to your account without compromising your cryptocurrency holdings. No cryptocurrencies can be stolen through a public address alone; theft can only occur if someone gains access to your private keys.
Bitcoin wallets differentiate between public and private keys. A public key is akin to an email address: anyone can send messages to it, but only the owner can read them. Similarly, others can use a cryptocurrency address to send funds, while the address owner is the sole individual who can access and use the digital assets.
Conversely, the private key serves as the password to access the wallet. It is essential to securely store this unique code offline, where no one can access it. Sharing sensitive information, such as private keys or wallet passwords, with others can result in the loss of your cryptocurrency holdings.
Therefore, it is advisable to share only your public key when necessary and safeguard other codes in a secure location.
How To Track Bitcoin Transactions
It’s not super difficult to trace Bitcoin transactions. Bitcoin blockchain technology ensures transparency, as all transactions are recorded on a distributed public ledger. This accessibility makes these transactions traceable by anyone. By employing tools called Bitcoin Explorers, users can monitor activity on the blockchain, including the amounts sent and the addresses involved in a transaction.
However, these transactions can only be traced to the user’s public key and do not reveal any real-world identification or personal information. Consequently, Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are more traceable than physical cash, primarily due to the blockchain ledger. In contrast, cash transactions lack a ledger: a $5 bill spent in a store today could end up on the other side of the world tomorrow without any record or trace of its journey.
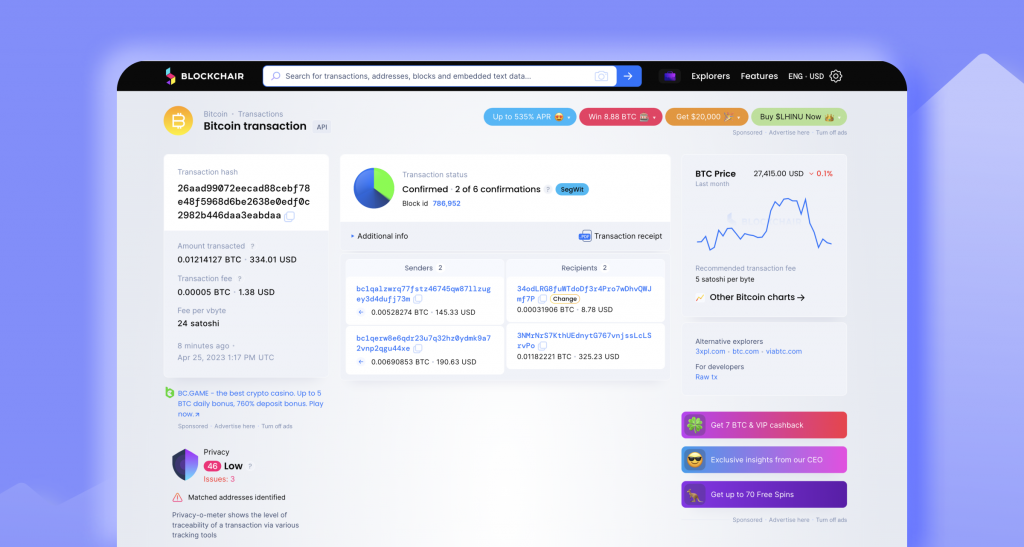
Tracking Bitcoin Transactions Step-By-Step:
To trace Bitcoin transactions on the blockchain, follow these steps using a tool like Blockchair:
- Visit blockchair.com and enter the Bitcoin address you want to trace in the search bar.
- Press enter to access a page containing all information related to the specified address.
- On this page, you can view all transactions made from the selected address, as well as the addresses to which funds have been sent.
- Additionally, you can see the block height, time, and date of each transaction. This information can be valuable in pinpointing specific transactions or identifying patterns in spending behavior.
By following these steps, you can easily explore the transaction history of a Bitcoin address, gaining insights into its activity and related addresses.
How Are Suspicious Crypto Transactions Reported?
Know Your Customer (KYC) is a standard practice in the financial services industry that helps protect against money laundering and other financial crimes. Institutions covered by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) must establish a clear relationship with clients and develop a “customer risk profile.” This profile is used to identify and report suspicious transactions to authorities.
Banks and other financial institutions are required to maintain customers’ personal information on file to be insured. Although the FDIC does not insure cryptocurrencies, US-based cryptocurrency exchanges have adopted KYC standards. Prominent exchanges such as Coinbase and FTX.US mandate customers to verify their identities. It is also worth noting that the FDIC, along with other regulatory agencies, is exploring the development of new legislation for crypto assets.
By adhering to KYC standards, cryptocurrency exchanges are better equipped to identify and report suspicious transactions, contributing to a safer and more regulated financial landscape.
What Makes Tracking Bitcoin Difficult?
Although it is widely acknowledged that Bitcoin transactions are not entirely anonymous and can be traced, some users have devised methods to make tracking their transactions more difficult.
One common approach to obscuring Bitcoin transactions is through the use of a Bitcoin mixer. This service mixes transactions from various wallets in a pool before sending them to a single address, making it significantly more challenging to trace the transactions.
Another method for impeding the tracing of Bitcoin transactions involves creating a smokescreen by establishing multiple crypto wallets and conducting numerous transactions between them. This tactic generates a complex loop, making it considerably harder to identify the wallet and trace individual transactions.
Despite these hurdles, tracking Bitcoin transactions is not impossible. However, it does require a substantial investment of time and effort to achieve this objective.
As a result, while users may employ various techniques to increase their transaction privacy, the inherent traceability of blockchain technology means that complete anonymity remains elusive.

Tips To Remain Anonymous With Crypto Transactions
Now, let’s explore essential tips and strategies to help you stay anonymous while conducting cryptocurrency transactions, ensuring your privacy and security in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
- Avoid Reusing Addresses
Always create a new address for each Bitcoin payment you receive and use that address exclusively for that specific transaction. This practice makes it more challenging for others to connect your payments and hinders attempts to track your activities.
- Don’t Use Your Real Name
When setting up a wallet, opt for a pseudonym rather than your actual name. This can be done by using a fake name or choosing an online wallet service that doesn’t require personal information.
- Be Cautious With Online Wallets
If you decide to use an online wallet service, select a reputable platform with robust security measures. It’s advisable to avoid storing large amounts of cryptocurrency in an online wallet. Instead, regularly transfer funds to a secure offline wallet for safekeeping.
- Consider Using Privacy-Focused Cryptocurrencies
Some cryptocurrencies, such as Monero, Zcash, and Dash, are specifically designed to enhance user privacy. These coins employ advanced privacy features that can make transactions more difficult to trace.
- Utilize VPN and Tor
When conducting Bitcoin transactions, consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) or the Tor network to obscure your IP address and further enhance your online privacy.
FAQs
- Are crypto transactions anonymous?
Cryptocurrency transactions, such as those with Bitcoin, are pseudonymous rather than anonymous, meaning wallet addresses replace real-world identities.
- How do cryptocurrency transactions work?
Cryptocurrency transactions involve transferring information between blockchain addresses, with transactions signed by private keys and validated by a network of nodes.
- Are Bitcoin transactions traced?
Yes, Bitcoin transactions can be traced using blockchain explorers, which show transaction details and public keys, though they do not reveal personal information.
- What makes tracing Bitcoin transactions difficult?
Tracing can be challenging through methods such as using Bitcoin mixers, creating multiple addresses, and carrying out various transactions.
- How can I remain anonymous when using Bitcoin?
To increase anonymity, avoid reusing addresses, use pseudonyms, exercise caution with online wallets, and consider using privacy-focused cryptocurrencies, VPNs, or the Tor network.
- Can I have an anonymous Bitcoin wallet?
While a completely anonymous Bitcoin wallet is difficult to achieve, certain wallets, like Electrum, can offer enhanced privacy when combined with other precautions.
- How do Bitcoin mixers work?
Bitcoin mixers work by pooling transactions from different wallets together and then sending them to a single address, making it difficult to trace individual transactions.
- Are there cryptocurrencies that offer better privacy than Bitcoin?
Yes, some cryptocurrencies like Monero, Zcash, and Dash are designed to enhance user privacy with advanced features that make transactions more difficult to trace.
Wrapping Up
Attaining total anonymity with cryptocurrency is difficult because of the built-in transparency of blockchain technology. Although you can take extra steps to make transactions harder to trace, true anonymity remains out of reach for most users.
That said, the chances of someone tracking your account, revealing your real-world identity, or freezing your assets are slim. These actions demand specialized tools and knowledge, often involving law enforcement agencies investigating criminal activities.
As a result, while cryptocurrency transactions may not provide perfect anonymity, they still offer a considerable degree of privacy and security for everyday users.



