What is the CryptoNight Mining Algorithm?
Cryptocurrency is an evolving trend that is expected to gain even more importance in the years to come. As of August 2022, Bitcoin is estimated to account for 60-77% of the world’s crypto-asset electricity consumption. According to the New York Times, BTC mining alone consumes approximately 0.5% of the total energy produced worldwide, which is also about seven times Google’s annual energy consumption, the newspaper reported.
With the rapid growth of crypto mining over the past few years, there have been countless mining algorithms developed.
One prominent mining algorithm is CryptoNight, known for its focus on privacy, resistance to ASIC mining, and scalability. In this guide, we will delve into the details of the CryptoNight algorithm, exploring its workings, significance, challenges, and the digital currencies that utilize it.
Key Takeaways:
- ASIC mining gained dominance due to the formidable power of ASIC chips, placing GPU miners at a disadvantage.
- CryptoNight is an algorithm that initially aimed to solve problems of ASIC centralization and traceability of transactions.
- ASIC miners have effectively adjusted to the CryptoNight algorithm, thus undermining its original objective.
- Some cryptocurrencies that operate on the CryptoNight algorithm include Bytecoin, HYCON and Electroneum.
Understanding Mining
Before diving into the specifics of CryptoNight, let’s first explore the concept of Proof of Work (PoW).
PoW is a consensus algorithm used in many blockchain systems, including the well-known Bitcoin, Litecoin and Dogecoin. Crypto transactions in such systems are confirmed by miners who solve complicated mathematical problems.

The process of mining begins with transactions being gathered together into a block. This block includes details such as the sender, recipient, amount, and timestamp of each transaction. Once the block reaches its maximum capacity, it is ready to be added to the blockchain.
In order for a miner to add this block to the blockchain, they must solve a complex cryptographic algorithm. This is done using powerful hardware, such as GPUs or ASIC miners (or cloud services), which perform countless calculations until a specific solution is found. This process is extremely energy-intensive and can require significant computing resources.
The first miner who successfully solves the algorithm and adds the block to the blockchain is rewarded with a certain number of coins.
In addition to receiving coins as a reward, miners also earn transaction fees for processing transactions. These fees can vary and are typically higher for transactions that require faster processing times.
ASICs vs. GPUs in Mining
Initially, when the concept of mining was introduced, the process was done with regular Central Processing Units (CPUs). It was advantageous for PC enthusiasts with high-end hardware, who could easily mine cryptos like Bitcoin and Ethereum v1.
However, as the popularity of Bitcoin grew and more people joined in, a new way of mining emerged – using Graphics Processing Units (GPUs). With GPUs being much faster than CPUs, crypto-mining became more accessible to a larger audience.
However, the situation changed with the arrival of ASIC miners in 2013. These Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) chips were specifically designed for specific purposes like mining coins and had much higher processing power compared to GPUs. As a result, they quickly outperformed their counterparts, causing a decline in GPU mining profitability.
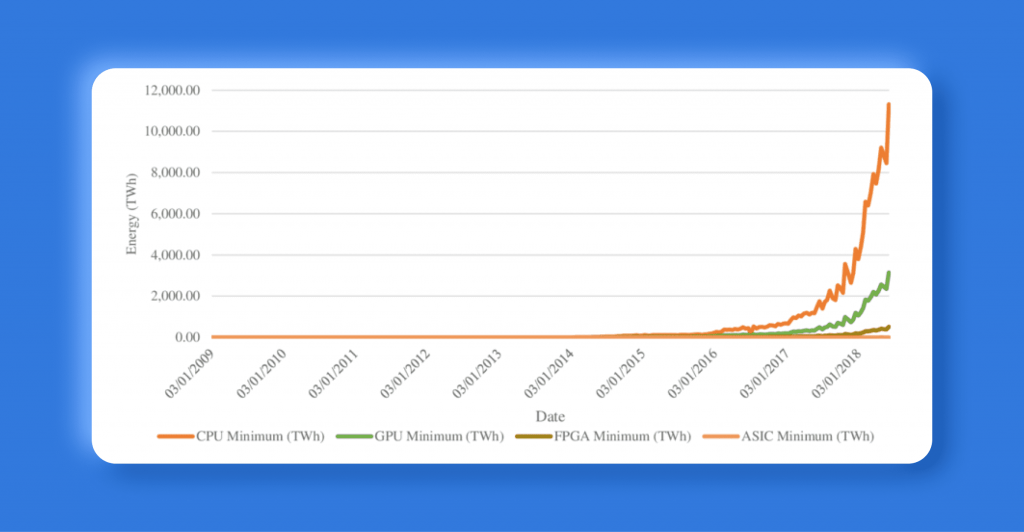
Bitcoin’s Proof of Work algorithm, SHA256, can be processed by both GPUs and ASIC miners. However, due to their specialized design, ASIC units have a significant advantage in efficiency over GPUs. This became evident with the release of Bitmain’s Antminer S9, which quickly became one of the most powerful and profitable ASIC miners on the market.
Fast Fact
With the rising popularity of mining and the booming crypto market, the demand for GPUs soared dramatically, even causing stock shortages in graphics card units. Both Nvidia and AMD, the giants of GPU manufacturing, experienced significant gains in their respective share prices during this period. However, in 2022, the crypto winter arrived, crashing BTC prices and rendering Bitcoin mining inefficient, resulting in graphic card prices plunging significantly.
What is CryptoNight?
CryptoNight is a proof-of-work hashing algorithm that was developed in 2013 as part of the CryptoNote protocol. It is specifically designed for PoW mining and stands out for supporting only CPUs and GPUs, making mining more accessible for regular computer hardware.
The creator of CryptoNight, known only by the pseudonym Nicolas van Saberhagen, remains a mystery and has disappeared from the public eye after the introduction of the algorithm. This adds to the intrigue surrounding CryptoNight’s origins, similar to how Satoshi Nakamoto’s identity is still unknown in the world of Bitcoin.
The main purpose of CryptoNight is to be ASIC resistant, unlike Bitcoin’s SHA-256 or Ethereum’s Ethash algorithms. This means that it is difficult or impossible to create specialized hardware for mining CryptoNight coins, making it more accessible for the general public to mine and participate in the network.

CryptoNight is a mining algorithm highly focused on security, utilizing the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), a military-level algorithm known for its strong encryption abilities. Thus, through its distributed and secure mining ecosystem, CryptoNight aims to maintain decentralization and fair competition for the mining community.
Another purpose of the algorithm is to provide privacy for individual transactions. While Bitcoin’s blockchain is publicly viewable, CryptoNight adds a layer of anonymity by making transactions more difficult to trace on the blockchain.
How Does CryptoNight Work?
To fully understand the workings of CryptoNight, let’s explore the core steps involved in the mining process.

Step 1
The first step in the CryptoNight mining algorithm is to create a “scratchpad”. This scratchpad is a large memory with intermediate values that are stored during the hashing function. The initial input data is hashed with the Keccak-1600 hashing function, resulting in 200 bytes of randomly generated data.
Step 2
After creating the scratchpad, the algorithm takes the first 31 bytes of this Keccak-1600 hash and transforms them into an encryption key for an AES-256 algorithm. This is considered to be the highest value within the AES family.
Step 3
Once the encryption transformation is complete, CryptoNight takes the entire data set created by the AES-256 and Keccak functions and passes it through the rest of the hash functions. This results in a final hash, which has a 256-bit extension or a total of 64 characters.
The Importance of CryptoNight
After the emergence of ASIC mining hardware, crypto mining has become increasingly centralized. These specialized hardware devices outperformed CPUs and GPUs, creating an unfair playing field for individual miners. CryptoNight intended to challenge this centralization by resisting ASIC dominance. Its design discourages the use of ASICs, promoting a more distributed and accessible mining ecosystem.
Another important aspect of this algorithm is privacy. While many cryptocurrencies, including BTC, have transparent and traceable transactions, CryptoNight prioritizes privacy. It integrates advanced privacy features such as ring signatures and stealth addresses. These features allow for untraceable transactions, ensuring maximum security and anonymity for users who value private blockchain transactions.
Finally, scalability is a critical factor for the growth and adoption of cryptocurrencies. CryptoNight addresses this by increasing computational requirements, allowing for faster transaction processing and improved scalability. This scalability ensures that a cryptocurrency can handle a larger volume of transactions efficiently, facilitating its widespread use and adoption.

The Challenges of CryptoNight
Despite its intention to be ASIC-resistant, CryptoNight has faced significant challenges in achieving this goal. The custom-made and specialized design of ASIC chips makes it nearly impossible to completely eliminate them from mining. Therefore, the only feasible solution has been to regularly fork the algorithm, forcing ASIC holders to invest in new hardware.
One such instance was in October 2018 when CryptoNight v7 was released with tweaked parameters to hinder existing ASICs. However, this tactic proved to be ineffective, as new ASICs were already detected by the end of December 2018. This pattern has continued with each fork, where ASIC dominance is temporarily suppressed only to return once the ASICs are modified.
The failure of CryptoNight to eliminate ASICs was highlighted in February 2019 in the Monero blockchain, which used the CryptoNight algorithm back then. It was found that over 85% of Monero’s mining power was dominated by ASIC hardware.
Despite its shortcomings, forking remains the most viable option for CryptoNight to delay ASIC domination. However, this approach comes with its own set of challenges. Regular updates through forking can lead to unwanted changes in the algorithm, which may de-anonymize transactions or even create new currencies. These issues were experienced in a 2018 fork of Monero, which created three new currencies (XMO, XMC, XMZ) and compromised its foundational principle of privacy.
Hence, CryptoNight has to navigate between two extremes – fighting against ASICs with regular forking while also maintaining the need for stability and consistency in the algorithm.
Cryptos Using the CryptoNight Algorithm
Several cryptocurrencies have adopted the CryptoNight algorithm for their mining processes. Let’s take a closer look at some notable examples:
Monero (XMR)
Monero is one of the most well-known cryptocurrencies that utilized the CryptoNight algorithm. It initially embraced CryptoNight to resist ASIC mining, aiming to maintain a more decentralized mining ecosystem. However, ASIC manufacturers quickly adapted, leading to a return of ASIC dominance in Monero mining. As a result, Monero transitioned to the RandomX algorithm. Nevertheless, Monero’s adoption of CryptoNight showcases the algorithm’s significance in promoting privacy and decentralization.
Bytecoin (BCN)
Bytecoin, launched in 2012, was the first cryptocurrency to implement CryptoNight. Initially, the project aimed to resist ASIC dominance by favoring CPU and GPU mining instead. However, as technology advanced and concerns arose, Bytecoin decided to integrate them into their mining process as well. While the project continues to explore GPU support, it recognizes that banning ASICs may not be a viable long-term solution.
HYCON (HYC)
Initially considering implementing the Blake2b hash function, the project ultimately stuck with CryptoNight due to its higher resistance to ASICs. They also plan on regularly changing their algorithm as a deterrent to potential ASIC miners and provide specific mining rigs for different hardware types.
Electroneum (ETN)
The next cryptocurrency on our list is Electroneum, which also started out using the original CryptoNight algorithm but later switched to CryptoNight v7 due to pressure from GPU miners. However, this move was met with mixed reactions within the community. One of its notable features is the inclusion of a mobile miner, allowing users to mine ETN using their mobile devices.
Dero (DERO)
Last but not least, Dero is another cryptocurrency that chose to stick with the original CryptoNight algorithm despite considering switching to Monero’s RandomX. The project cited concerns about security during testing and dependencies on chip manufacturers as reasons for their decision.
Other Projects
The CryptoNight algorithm has been implemented in a variety of cryptocurrency projects. However, in 2017, several projects using the CryptoNight algorithm were targeted by malicious attacks, raising concerns about its reliability. This has prompted developers to create different variants of the algorithm in order to address these vulnerabilities.
One such variant is CryptoNight Heavy, which is used by projects like Ryo Currency, Sumokoin and Loki. However, it has been noted that this implementation may also have its own drawbacks. Since CryptoNight Heavy relies on a trustless peer-to-peer network, it may be more susceptible to distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. These coordinated attacks overwhelm a network with fake traffic, making it difficult for nodes to function properly and validate new blocks.
Conclusion
Despite all the challenges, developers continue to explore the potential of the CryptoNight algorithm and work towards improving its security. Its implementation in various cryptocurrency projects shows its significance in promoting privacy and decentralization. However, there is still a question as to whether the algorithm can truly achieve its goal of being ASIC-resistant. Nevertheless, the CryptoNight algorithm remains an essential part of the crypto industry and a great foundation for future blockchain projects, particularly those that emphasize privacy and fairness.
FAQs
How do Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake algorithms differ?
Proof of Work and Proof of Stake are two common consensus algorithms used in blockchain networks. They function differently from each other. In PoW, miners compete against each other to perform complicated calculations using powerful computers. In contrast, PoS relies on validators who are selected according to their stake.
Is GPU mining dead today?
No, GPU mining is not dead. It is still a popular method of mining for certain coins. However, it may not be as profitable as it once was due to the increase in difficulty and competition. Additionally, some cryptocurrencies now prefer more advanced mining equipment, such as ASICs, over GPUs. Moreover, the recent decline in crypto prices has also affected the profitability of GPU mining.
What mines faster: CPU or GPU?
GPU mining is far from dead. It remains a popular mining method for specific tokens. However, due to heightened difficulty and competition, it may not be as lucrative as it once was. Furthermore, certain cryptocurrencies now favor specialized mining hardware like ASICs over GPUs. Additionally, the recent decline in crypto prices has impacted the profitability of GPU mining.



