How to Identify a Crypto Ponzi Scheme
In a world where Bitcoin turned early investors into millionaires, the allure of cryptocurrency riches has created fertile ground for fraudsters. While legitimate cryptocurrency projects continue to innovate and reshape the financial landscape, bad actors exploit investors’ fear of missing out (FOMO) through sophisticated Ponzi schemes disguised as revolutionary crypto investments.
This article will equip you with the knowledge to identify a crypto Ponzi scheme and safeguard your investments. We’ll delve into the key characteristics of these scams, explore the crucial differences between Ponzi and pyramid schemes, and provide actionable tips to help you steer clear of such schemes.
Key Takeaways
- Crypto Ponzi schemes lure investors with unrealistic promises of high returns and minimal risk.
- These schemes are unsustainable and eventually collapse, leaving early investors with profits while later investors lose everything.
- By understanding the red flags and doing thorough research, you can protect yourself from falling victim to a crypto Ponzi scheme.
What Is a Crypto Ponzi Scheme?
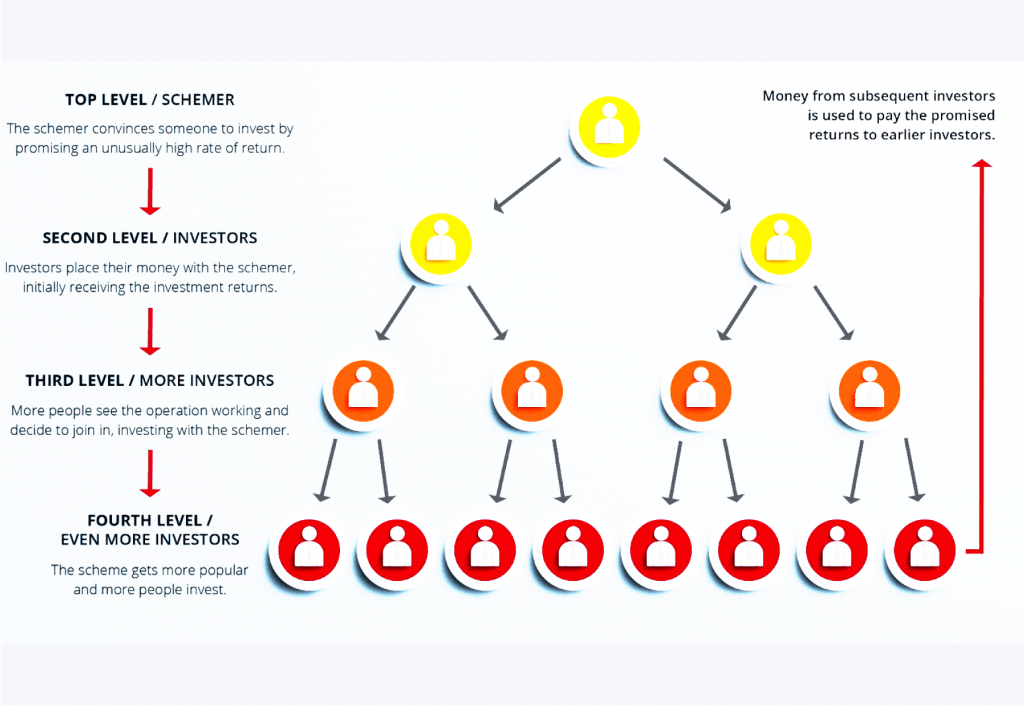
A Ponzi scheme, named after Charles Ponzi, is a fraudulent investment operation that pays investors returns from funds from new investors’ contributions. There’s no underlying legitimate business activity generating these returns. Instead, the scheme relies on a continuous flow of new money to sustain payouts to earlier investors, creating an illusion of profitability.
Crypto Ponzi schemes operate on the same principle but target the cryptocurrency market. Scammers entice investors with promises of guaranteed high returns on their crypto investments, often with minimal or no risk.
These schemes often prey on people with a limited understanding of cryptocurrency and the inherent risks involved.
Fast Fact
Charles Ponzi’s name became synonymous with financial fraud in the 1920s after orchestrating a notorious investment scam in the United States. While claiming to profit from international postal coupon trading, he paid earlier investors with new investors’ money, attracting massive sums before the scheme’s collapse. The extensive media coverage of his fraud, both during and after its exposure, led to such deceptive investment schemes being permanently labeled as “Ponzi schemes.”
Ponzi Scheme vs. Pyramid Scheme
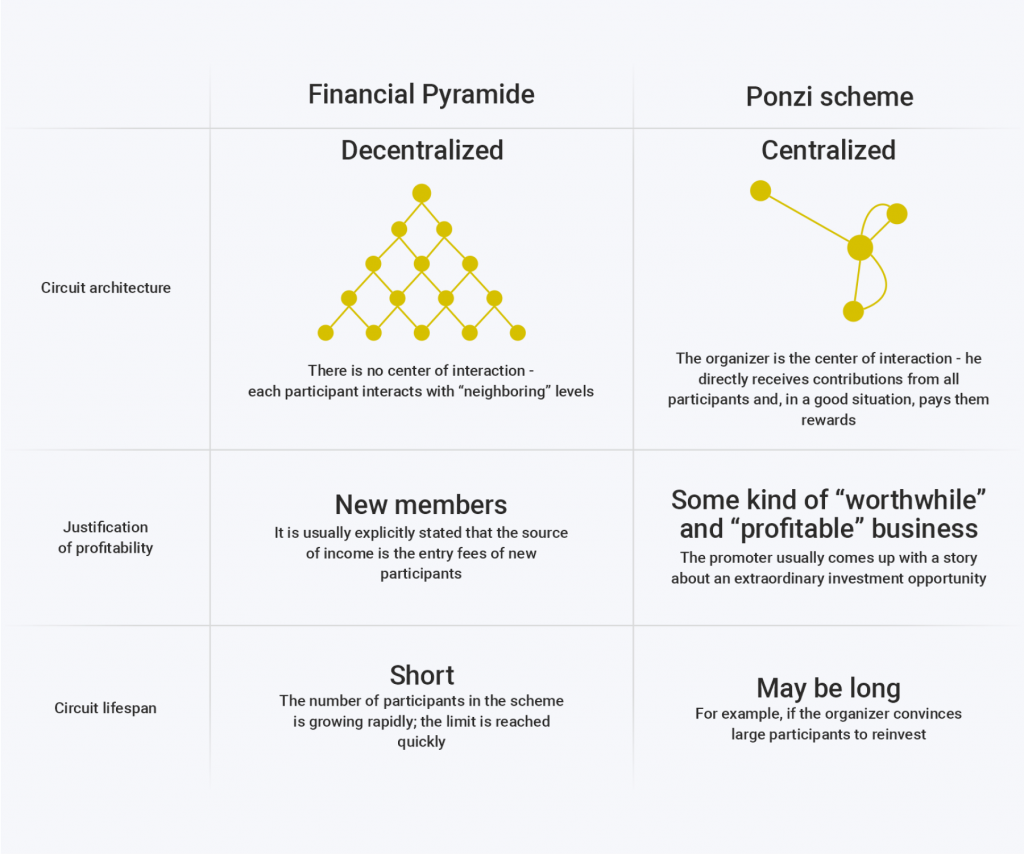
It’s important to distinguish between Ponzi and pyramid schemes, although both are fraudulent investment scams.
In a Ponzi scheme, participants invest in a centralized source, often managed by a portfolio manager or scammer. Returns are paid to earlier investors from funds contributed by newer investors. There is no actual product or investment.
In a pyramid scheme, participants earn by recruiting others, often selling overpriced or non-existent products. Pyramid schemes are structured in layers where each participant must bring in additional recruits, creating a hierarchical network where only the top few make significant money.
Here’s a breakdown of the key differences:
- Focus: Ponzi schemes focus solely on investments, promising high returns on invested capital. Pyramid schemes, on the other hand, center around recruitment, encouraging participants to recruit new members to earn money, often with minimal or no actual product or service involved.
- Structure: Ponzi schemes are typically run by a single entity that controls the flow of funds. Pyramid schemes involve a hierarchical structure with multiple levels of participants, where those at the top benefit from recruiting new members below them.
- Sustainability: Ponzi schemes can continue as long as new investor money comes in to pay earlier investors. Pyramid schemes, however, become unsustainable much faster as recruiting new members becomes increasingly tricky.
How to Identify Cryptocurrency Scams
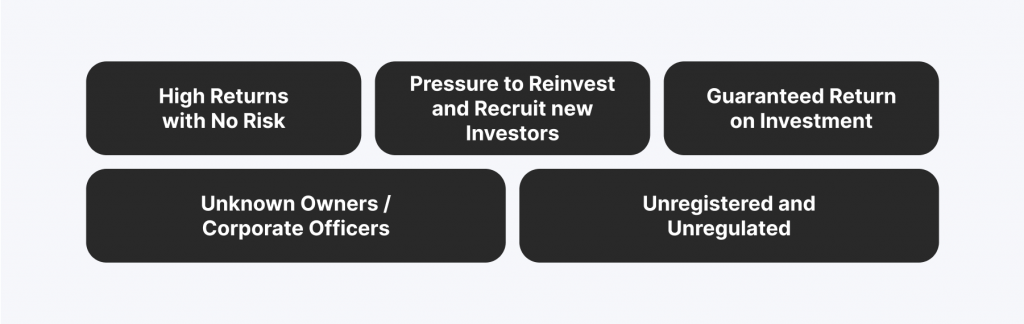
Identifying a crypto Ponzi scheme can be challenging, but several red flags can signal that an investment opportunity might be a scam:
- Guaranteed High Returns: If an investment promises guaranteed high returns with little to no risk, it’s likely a scam. Legitimate investments always carry some level of risk, and returns are never guaranteed.
- Unrealistic Profit Margins: Be wary of schemes that promise astronomical profits in a short period. The cryptocurrency market can be volatile, and significant and consistent returns come with associated risks.
- Lack of Transparency: Legitimate crypto projects are transparent about their team, technology, and development roadmap. A red flag is a project with limited or no information about its creators or its intended use.
- Pressure to Invest Quickly: Scammers often pressure potential investors to invest quickly before “missing out” on a great opportunity. This tactic is designed to prevent you from conducting thorough research.
- Pressure to Recruit New Investors: Ponzi schemes often require participants to recruit new investors to sustain returns. If an investment opportunity greatly emphasizes bringing in others, it’s a significant warning sign.
- Difficulty Withdrawing Funds: If a platform makes it difficult to withdraw your funds, it’s a major red flag. Legitimate exchanges allow for easy and transparent withdrawals.
Famous Crypto Ponzi Schemes
While Charles Ponzi gave his name to the infamous fraud scheme, similar scams existed decades earlier. In Germany, Adele Spitzeder ran such a scheme from 1869-1872, while Sarah Howe targeted American women in the 1880s through her “Ladies’ Deposit,” promising 8% monthly returns before stealing their investments and eventually serving prison time. Interestingly, Charles Dickens had already portrayed similar fraudulent schemes in his novels “Martin Chuzzlewit” (1844) and “Little Dorrit” (1857), showing that these deceptive practices were well-known enough to appear in popular literature.
The field of cryptocurrency has witnessed numerous Ponzi schemes, where investors lose substantial amounts of money. Notable examples include BitConnect, which promised high returns and ended up being one of the largest cryptocurrency Ponzi schemes to date, and PlusToken, which targeted millions of people across multiple countries.
Crypto Ponzi Scheme List: Common Types and Tactics
Fake Trading Platforms: These platforms mimic legitimate cryptocurrency exchanges, claiming to offer high returns through automated trading. Instead, they take investor money and disappear.
Ponzi Coin Offerings: These schemes attract new investors by issuing tokens, which are touted as revolutionary digital currencies. However, the money raised is often used solely to pay returns to existing investors.
Mining Scams: Certain schemes entice users by claiming to offer cloud-based mining services. In reality, these operations are fake, using funds from new participants to pay returns rather than actual mining.
How Crypto Ponzi Schemes Work: Step-by-Step
The crypto market’s relative newness and lack of regulatory oversight make it ripe for exploitation. The allure of cryptocurrency’s volatility can make “high returns” seem plausible, drawing in those less familiar with digital assets.
Additionally, the decentralized nature of crypto transactions enables scammers to steal money while staying relatively anonymous, evading regulatory bodies like the Securities and Exchange Commission or the Federal Bureau of Investigation.
Here’s a typical structure of this scheme:
- Attracting Investors: Scammers advertise high-yield opportunities, often promising low-risk, high-return investment plans.
- Encouraging Reinvestment: Many schemes encourage existing investors to reinvest their “earnings” for compounding returns, which only benefits the scammers.
- Targeting New Investors: To sustain payouts to earlier investors, these schemes continually seek new participants, creating a cycle that can last until recruitment stalls.
- Collapse: When recruitment slows or a substantial number of investors attempt to withdraw, the scheme collapses, leaving victims with significant losses.
How to Protect Yourself from Cryptocurrency Scam

To safeguard your investments from phishing scams, consider these essential tips:
- Research and Verify: Conduct thorough research on the platform or person proposing the investment. Check online reviews, visit official websites, and consult regulatory sources.
- Avoid High-Pressure Sales Tactics: Scammers often employ pressure tactics to encourage quick decisions. Legitimate investments allow time for due diligence.
- Consult Financial Experts: A reputable portfolio manager or financial expert can help assess the legitimacy of a potential crypto investment.
- Look for Regulatory Approval: Scams typically avoid official registration. For example, legitimate businesses in the U.S. are registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission or equivalent regulatory bodies.
- Use Secure Payment Methods: Avoid payment methods like wiring funds to unknown bank accounts. A legitimate crypto digital wallet offers a transparent transaction history.
If you suspect you’ve been involved in a crypto Ponzi scheme, report it immediately to the Internet Crime Complaint Center or local financial regulatory authorities. Keep all evidence of your transactions and communications with the scammers. This documentation can aid in a potential investigation and increase the likelihood of recovering your lost funds.
Conclusion
While cryptocurrency offers legitimate investment opportunities, the sector’s rapid growth and technical complexity make it attractive to fraudsters. By understanding the warning signs of crypto scams and following proper due diligence procedures, investors can better protect themselves while participating in the digital asset revolution.
Remember: If an investment opportunity sounds too good to be true, it probably is. Legitimate cryptocurrency projects focus on technology and utility rather than guaranteed returns and recruitment.
FAQ
Is crypto a Ponzi scheme?
One of the biggest misconceptions about Bitcoin is that it is a scam similar to various Ponzi and pyramid schemes. This is a consequence of multiple reasons, one being that very few people understand what a Ponzi scheme is, and there is a solid reason to believe that even fewer people understand Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies.
Is crypto a pyramid scheme?
Bitcoin and cryptocurrency are not pyramid schemes or frauds. Even though there have been instances of fraud in the cryptocurrency world, it’s critical to discern between scams and real coins.
What is a securities fraud?
The term Securities Fraud covers a wide range of illegal activities, all involving the deception of investors or the manipulation of financial markets. Characterized by promises of high rates of return with little or no risk.