Why Your DeFi Experience Is Incomplete Without an Ethereum Wallet
Undeniably, the crypto industry has grown and evolved in ways we couldn’t have predicted a few years ago. Ethereum, the second-largest blockchain by market capitalization, is a clear testament to this expansion. Although Ethereum might be the runner-up in terms of sheer size, it undoubtedly takes the lead when it comes to the sheer volume and variety of applications and Decentralized Finance projects it hosts.
Ethereum’s reach and influence are vast. Over 230 million unique addresses have been created on its network, demonstrating how ingrained it has become in the crypto and blockchain universe. Given Ethereum’s wide-ranging applications, it’s increasingly important for anyone involved in the crypto world to own an Ethereum wallet address.
But why exactly is an Ethereum wallet so crucial today? What does it bring to the table, and why is it quickly becoming a must-have for anyone?
Key Takeaways
- Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform hosting various dApps and powered by its native cryptocurrency Ether (ETH).
- An Ethereum wallet is a digital tool for managing Ethereum-based assets, holding a pair of cryptographic keys: a public key for receiving funds and a private key for authorizing transactions.
- ETH wallets come in different forms, including online, mobile, desktop, hardware, and paper wallets, adjusting to different needs and security preferences.
- Popular Ethereum wallets include Trust Wallet, MyEtherWallet (MEW), Trezor, Exodus, and MetaMask, offering usability, security, and comprehensive features for managing Ethereum assets.
Exploring Ethereum: A Comprehensive Introduction
Ethereum is a decentralized platform backed by its unique blockchain and ecosystem. The idea of decentralization infers that no single, trusted central authority manages the network. This framework allows users to develop decentralized applications, implement smart contracts, and even bring new cryptocurrencies. Ethereum is also instrumental in creating decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), safeguarding assets, and facilitating transactions without intermediaries.
The Ethereum blockchain ensures that transaction records are immutable, transparent, and securely disseminated. This feature makes Ethereum an effective tool for tracking the ownership of digital currencies and ERC-20 tokens.
All participants on the network can access and view transaction data, offering a streamlined approach to prevent fraudulent activity. When it comes to personal information, Ethereum enables users to have full control over their data and how much of it is shared.
Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency, ETH, acts as the payment medium for network activities. Ethereum proudly stands as one of the world’s largest cryptocurrencies.
Applications Of The Ethereum Blockchain
Ethereum is popular with its broad use cases and applications, here are a few examples.
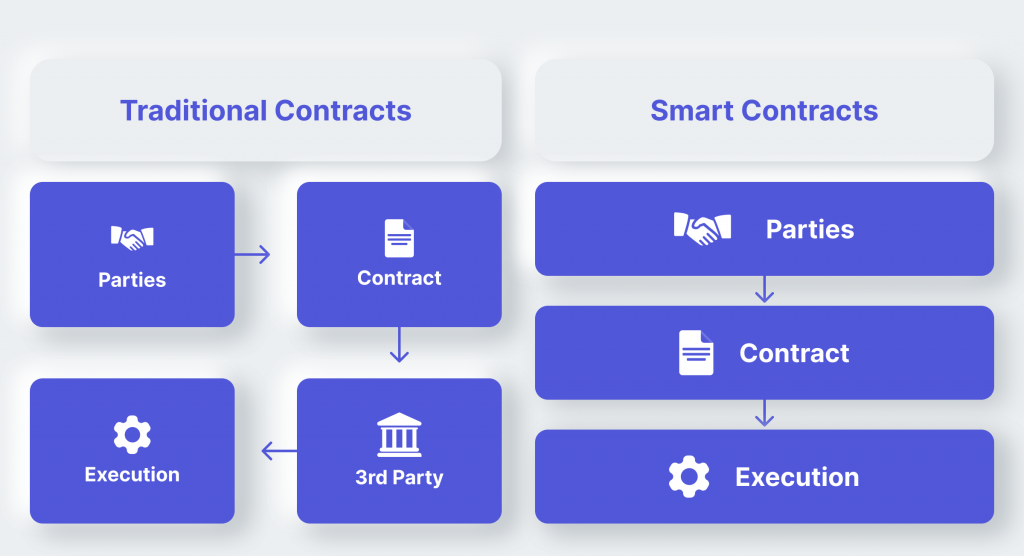
1. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts represent an innovative protocol to enable digital contracts without third-party validation. These autonomous contracts encode the buyer-seller agreement directly into lines of code.
The execution of smart contracts on Ethereum is decentralized, with anonymous parties in the network facilitating the verification process. This removes the need for a central authority. The asset and currency transfers are secure and trustworthy, with the entities’ identities safely concealed within the network.
The accounts are automatically updated upon transaction completion, fostering trust between parties.
2. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Ethereum’s rise to fame is largely attributable to its DeFi capabilities. DeFi, or decentralized finance, allows payment execution without reliance on financial institutions or banks. The DeFi ecosystem has constructed a vast network of integrated protocols and financial instruments, locking over $13 billion worth of value into Ethereum’s smart contracts.
3. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
Non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, have revolutionized the digital art creation realm. NFTs serve to prove ownership of unique items. These tokens are instrumental in tokenizing and declaring ownership of various things, such as artwork, collectibles, and even real estate.
As ensured by the Ethereum blockchain, an NFT can have only one official owner at any given time, and it is impossible to duplicate an NFT or modify the record of ownership.
Ethereum provides digital certificates for these unique assets, validating unique ownership that cannot be transferred. While copies of these digital assets may exist, NFTs are traceable on blockchains to provide the owner with proof of original ownership.
4. Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Decentralized applications, commonly known as dApps, are developed and powered via the Ethereum platform. They utilize smart contracts for their logic and are deployed on the Ethereum network, utilizing the platform’s blockchain for data storage.
dApps are as diverse as their traditional mobile and web application counterparts, offering a range of functions, including social networks, gaming, entertainment, productivity, and more. Many dApps are specifically designed to assist users in accessing DeFi services. Such popularity has led Ethereum to categorize dApps into financial, semi-financial, and other categories.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Ethereum Wallets
An Ethereum wallet essentially acts as an application or software program enabling you to harbor the necessary data to access your Ether funds safely. Keeping your Ethereum holdings on a crypto exchange can prove risky due to potential vulnerabilities such as exchange hacks or sudden closures, which could result in the loss or theft of your cryptocurrency.
The Functioning of Ethereum Wallets
The principle behind every Ethereum wallet lies in a private key, a cryptographic element that grants you access to your funds. In this context, there are two keys to consider: the public and private keys. The public key functions as an address, a unique identifier you employ when transferring funds from one account or wallet to another. Conversely, the private key confirms your identity to the network, effectively signaling that you are the rightful owner of those coins.
Wallets housing the private key are secured with a password, a necessary component to access your Ether coins. Ethereum maintains a ledger of the amount of ETH coins linked to every private key on the blockchain. Hence, as a user, you must possess that password-protected key to access your coins.
A secure wallet for Ethereum stores these keys in an encrypted format, which can only be decrypted with a user-defined password. Given the absence of a ‘forgot password’ feature, it is crucial not to forget your password. Ideally, it should be recorded somewhere secure, like a notebook. It’s also a good practice to create a backup of your private keys, which can be stored on various mediums such as a USB drive, a physical piece of paper, an alternative server, or another digital ledger.
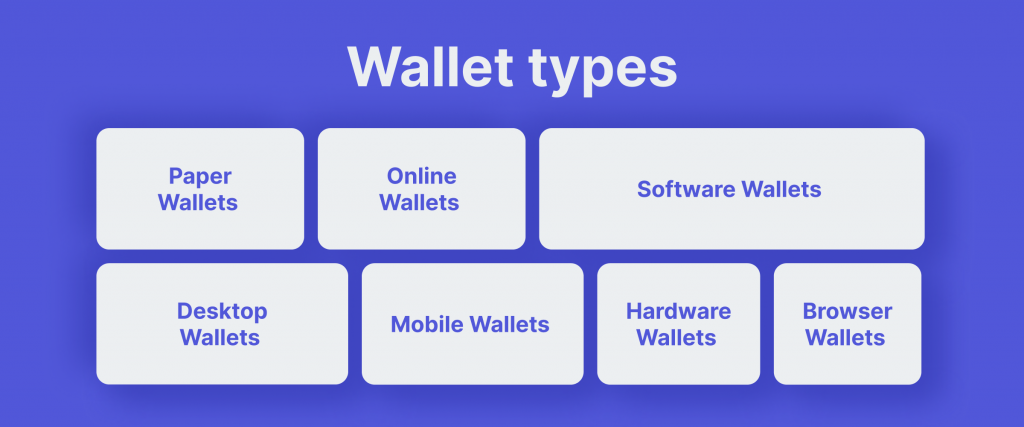
Various Types of Ethereum Wallets
Ethereum wallets come in multiple forms, each with its own unique features and use cases.
- Paper Wallets
An Ethereum paper wallet is simply a piece of paper on which the private and public keys are printed. It doesn’t require an internet connection to store keys, thereby providing some level of protection from online threats. However, the material fragility of paper makes it less suitable for long-term storage.
- Online Wallets
Online Ethereum wallets are typically hosted on centralized services such as crypto exchanges. While these wallets are user-friendly, their centralized nature means a substantial risk of losing all digital assets to cyberattacks or fraudulent websites.
- Software Wallets
Software Ethereum wallets offer a balance between security and convenience. They allow for frequent transactions and ensure that the user solely controls their private keys, thereby reducing hacking risks. However, they fall short of the security provided by paper or hardware wallets.
- Mobile Wallets
Mobile Ethereum wallets are lightweight and easily installed on mobile devices. They allow users to manage their funds using a cellular connection. While convenient, they are more susceptible to security breaches. Thus, it’s wise to store only small amounts of ETH for daily use and regularly back up the wallet.
- Hardware Wallets
Hardware Ethereum wallets are akin to flash drives that store users’ private keys offline. While these wallets offer robust security, they can be cost-prohibitive for users who only store small amounts of crypto. Purchasing new hardware wallets is also crucial, as secondhand or third-party wallets could be compromised.
- Browser Wallets
Browser wallets store ETH and ERC-20 tokens and enable interaction with decentralized applications. While they offer a relatively secure alternative to web interfaces, they are not recommended for long-term storage of substantial funds.
- Desktop Wallets
Desktop Ethereum wallets operate on various operating systems, enabling users to send and receive Ethereum, create smart contracts, and more. While these wallets rely on internet connections, thus posing some risk, using a full client can increase security by independently validating transactions.
The Importance of Having an Ethereum Wallet
There are several compelling reasons for choosing to own an Ethereum wallet.
- Enhanced Security of Assets
At the core of Ethereum wallet benefits is its enhanced safety for digital assets. Compared to centralized exchanges or custodial wallets, where users must relinquish control over their private keys, an Ethereum wallet offers superior protection. The wallet allows users to store their private keys independently, thus significantly mitigating the risk of theft or hacking.
- Seamless Interaction with DeFi Applications
DeFi, with its decentralized take on traditional financial services like lending and trading, has significantly transformed the financial landscape. As these applications run on the Ethereum blockchain, interacting with the DeFi universe requires an Ethereum wallet. This wallet facilitates effortless connectivity with DeFi protocols, permitting deposits, withdrawals, yield farming, and liquidity provision, among other operations.
- Efficient Token Management
An Ethereum wallet offers a hassle-free way to manage Ethereum-based tokens. With an intuitive interface, users can view balances, transfer and receive tokens, and track transaction history for diverse digital assets, including Ethereum’s native coin, ETH, and various ERC-20 tokens. This simplicity is invaluable for traders, investors, or individuals holding Ethereum-based assets.
- Gateway to the Metaverse and NFTs
The rise of NFTs representing unique digital assets, such as art pieces, collectibles, and virtual real estate, has necessitated Ethereum wallets. Given that most NFTs are minted on the Ethereum blockchain, these wallets are crucial for storing and trading these digital collectibles.
- Privacy and Anonymity
Even though the Ethereum network itself is pseudonymous, with transactions traceable back to wallet addresses, Ethereum wallets can offer users increased privacy and anonymity. Some wallets incorporate features like currency mixing, multi-signature transactions, and privacy-focused technologies, allowing users to control their financial privacy. An Ethereum wallet enables individuals to execute transactions without unnecessarily revealing their personal information, promoting a secure and private experience.
- Interoperability and Flexibility
Ethereum wallets not only interact with the Ethereum blockchain but can also support many Ethereum-based tokens, including ERC-20 and ERC-721 (NFTs). This capability extends the wallet’s usefulness across a broader range of applications, allowing users to store and manage a diverse portfolio of digital assets in a single place.
- Direct Ownership
Unlike traditional banking systems, where the bank holds your money and acts as an intermediary for transactions, an Ethereum wallet gives you direct ownership of your digital assets. This decentralized feature of cryptocurrency wallets removes the need for intermediaries and gives users more control over their assets.
- Cost Efficiency
Transaction costs for sending and receiving digital assets through an Ethereum wallet can be significantly lower than traditional financial systems, especially for cross-border transfers. This is particularly advantageous for those who regularly engage in international transactions.
- Potential for Earning Interest
With the rise of DeFi, many Ethereum wallets now offer the potential to earn interest on your assets through staking or lending protocols. This can serve as an additional income stream for crypto asset holders, another feature not commonly found in traditional financial systems.
Choosing the Right Ethereum Wallet for You
The ideal Ethereum wallet should combine user-friendliness with a high level of security and allow its users to engage fully with the Ethereum ecosystem. Here are five Ethereum wallets that meet these criteria:

1. Trust Wallet
Trust Wallet is a versatile mobile crypto wallet supporting millions of digital assets, including Ethereum. Although it can’t be converted directly to cold storage, it allows users to buy, stake, and exchange assets directly from the app. Trust Wallet also gives users the ability to access Ethereum dApps and manage a range of digital assets, including NFTs, through an integrated mobile browser. Notably, Trust Wallet doesn’t store users’ private keys, ensuring high security and privacy.

2. MyEtherWallet (MEW)
MyEtherWallet is a free, open-source web wallet designed for Ethereum, Ethereum Classic, and ERC-20 tokens. It doesn’t require any software installation and provides a mobile app for Android and iOS. The private key is stored securely in an encrypted file on your device. MEW supports smart contract interaction and provides an exchange service for ETH to BTC. However, remember that users are responsible for recovery passwords, as MEW doesn’t support lost funds.

3. Trezor
Trezor is a hardware wallet compatible with various operating systems and supports multiple cryptocurrencies, including Ether and ERC-20 tokens. This compact device, which resembles a flash drive, ensures enhanced security with two-factor authentication and encryption features. Your digital assets are stored on a secure electronic chip activated with a unique PIN. Trezor also allows you to engage with dApps by integrating with desktop applications.

4. Exodus
Exodus is a multi-asset crypto wallet accessible via both desktop and mobile platforms. Besides storing and managing Ethereum and Ethereum-based tokens, Exodus allows users to earn staking rewards, trade cryptocurrencies through its in-built exchange, and earn interest by depositing their assets in a DeFi lending protocol.
Exodus doesn’t store your private keys, making you the sole custodian of your funds. In addition, Exodus includes features such as seed key backup and one-click email recovery.

5. MetaMask
MetaMask is a browser-based wallet that lets users access their Ethereum wallet through a browser extension or a mobile app. It enables interaction with dApps without installing a full node, making it an ideal choice for those who wish to participate in token staking.
As a non-custodial wallet, MetaMask stores users’ private keys in an encrypted format in the browser without transmitting them elsewhere.
MetaMask also safeguards users against phishing threats and immediately alerts you if you interact with a flagged website.
Conclusion
Owning an Ethereum wallet is essential for anyone seeking to engage with DeFi and other Ethereum-based services. Through an Ethereum wallet, individuals gain access to a decentralized economy, benefiting from secure asset storage, seamless token management, participation in the NFT market and the metaverse, privacy, anonymity, and the opportunity to explore upcoming advancements.
FAQs
Can I use the same Ethereum wallet for different cryptocurrencies?
Most Ethereum wallets are designed for Ethereum and Ethereum-based tokens, though some may support a limited number of other cryptocurrencies.
What should I do if I lose access to my Ethereum wallet?
If you lose access to your Ethereum wallet, recovery can be challenging. It is important to follow backup procedures, securely store recovery information, and consider wallets that offer recovery options or customer support. Regular backups and safeguarding recovery information are crucial to prevent permanent loss of funds.
Can I access my Ethereum wallet from my phone?
The accessibility of an Ethereum wallet across multiple devices depends on the wallet type, with some offering multi-device support while others require a physical connection.



