ETF vs ETP in Crypto: Differences and Advantages
The augmenting field of cryptocurrency can be a thrilling yet scary space for investors. While the potential for high returns is undeniably attractive, the complexities of navigating crypto exchanges and securely storing digital assets can be daunting.
This is where Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and Exchange-Traded Products (ETPs) occur as compelling alternatives. Understanding the differences between these financial instruments, as well as their key advantages, is crucial for both novice and experienced investors.
This guide will delve into the specifics of ETF vs ETP in crypto, providing you with the knowledge needed to make informed investment decisions.
Key Takeaways
- ETFs and ETPs offer convenient ways to invest in cryptocurrencies without directly buying or storing them.
- ETFs are a specific type of ETP that tracks an underlying basket of assets, while ETPs encompass a broader range of financial instruments.
- Crypto ETFs invest directly in cryptocurrencies, while some ETPs use derivative contracts like futures to track crypto prices.
- Both ETFs and ETPs offer advantages, such as diversification, liquidity, and potentially lower fees, compared to directly buying crypto.
Understanding ETFs vs. ETPs in Crypto
Before discussing the advantages and differences between these assets, let’s define both of them.
What is a Crypto ETF?
A crypto ETF is a type of investment fund traded on stock exchanges, much like a stock. It holds assets such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, or other cryptocurrencies and aims to track their performance. Investors can buy shares of the exchange-traded fund, which represents a proportional stake in the underlying assets. This allows investors to gain exposure to the price movements of cryptocurrencies without the complexities of managing digital wallets and private keys.
What is a Crypto ETP?
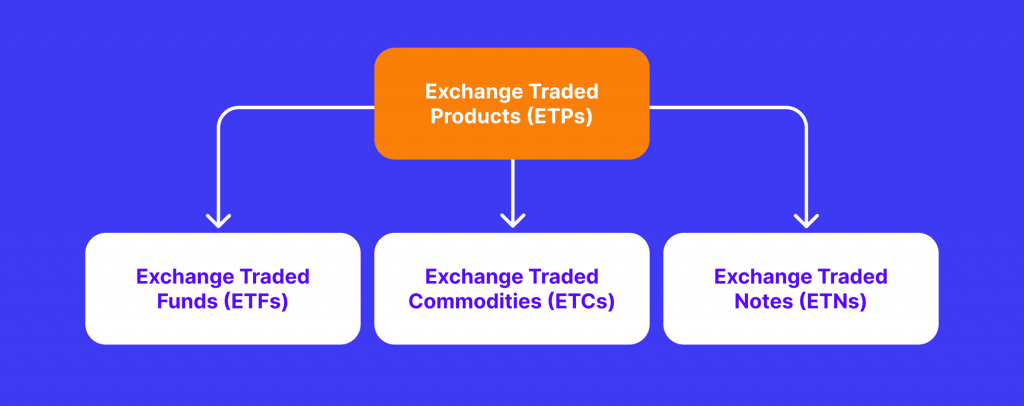
Crypto ETPs, or Exchange-Traded Products, are a broader category of financial instruments that can include ETFs, ETNs (Exchange-Traded Notes), and ETCs (Exchange-Traded Commodities). ETPs are designed to provide investors with exposure to an underlying asset, such as a cryptocurrency, by issuing securities that trade on exchanges. Crypto ETPs can track the price of individual cryptocurrencies or a basket of digital assets.
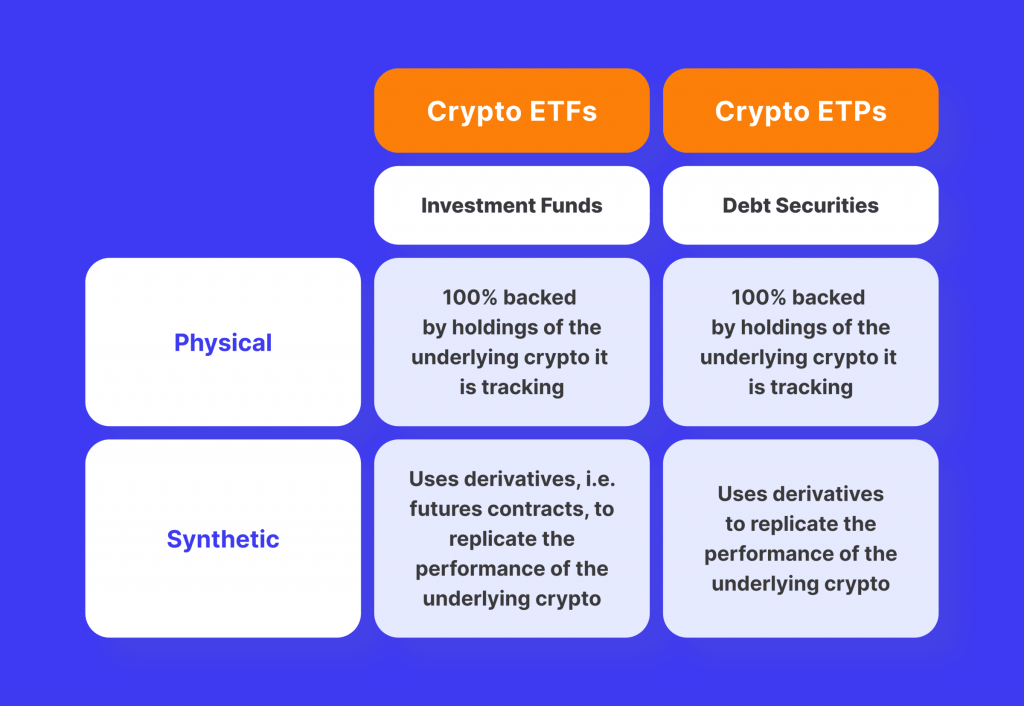
Key Differences Between Crypto ETFs and ETPs
While both ETFs and ETPs offer convenient ways to gain exposure to cryptocurrencies, there are some key distinctions to understand:
Structure
ETFs are a specific type of exchange-traded product that tracks an underlying basket of assets, which can be a single cryptocurrency, a basket of cryptos, or even a combination of cryptos and other traditional assets.
ETPs, on the other hand, encompass a broader range of financial instruments, including Exchange-Traded Commodities that track physical commodities like gold and Exchange-Traded Notes, which are essentially debt securities issued by a financial institution.
Underlying Asset
Crypto ETFs directly invest in the underlying cryptocurrency, meaning the fund actually holds digital assets. For example, a Bitcoin ETF holds Bitcoin or Bitcoin futures contracts.
Conversely, some ETPs, particularly those focused on Bitcoin, may utilise derivative contracts like futures to track the price of the cryptocurrency without holding the actual coins. Crypto ETPs might hold cryptocurrencies, futures, or even debt instruments issued by companies in the crypto industry. This broader definition allows for more diverse investment strategies but can also introduce additional risks.
Regulation
ETFs are regulated under the Investment Company Act of 1940 in the U.S., providing a higher level of investor protection and transparency. They are required to hold the underlying assets or equivalent value.
ETPs, on the other hand, are not confined to the same stringent regulatory standards. This category includes ETNs and ETCs, which can involve different structures and risk profiles.
Investment Strategy
ETFs typically aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index or a basket of assets. For instance, a Bitcoin ETF aims to mirror the price of Bitcoin.
ETPs can follow various strategies, including tracking individual asset prices, baskets of assets, or employing leverage and inverse strategies.
Tax Efficiency
ETFs generally offer better tax efficiency due to their structure, which allows for in-kind redemptions and creations. This process can minimise capital gains distributions to investors.
ETPs may not always offer the same tax advantages, depending on their specific structure and the regulations they are subject to.
Advantages of Crypto ETFs and ETPs
Whether you choose a crypto ETF or ETP, you benefit from several significant advantages:
- Diversification: Instead of putting all your eggs in one basket by buying a single cryptocurrency, ETFs and ETPs allow you to gain exposure to a broader market segment, potentially mitigating risk.
- Liquidity: Both ETFs and ETPs trade on traditional stock exchanges, offering the same level of liquidity as stocks. You can easily buy and sell your holdings throughout the trading day.
- Regulation: Crypto ETFs and ETPs are regulated financial products, which means they must adhere to strict guidelines and undergo regular audits.
To be more precise, let’s outline the benefits of ETFs and ETPs separately and in detail.
Key Advantages of Crypto ETFs
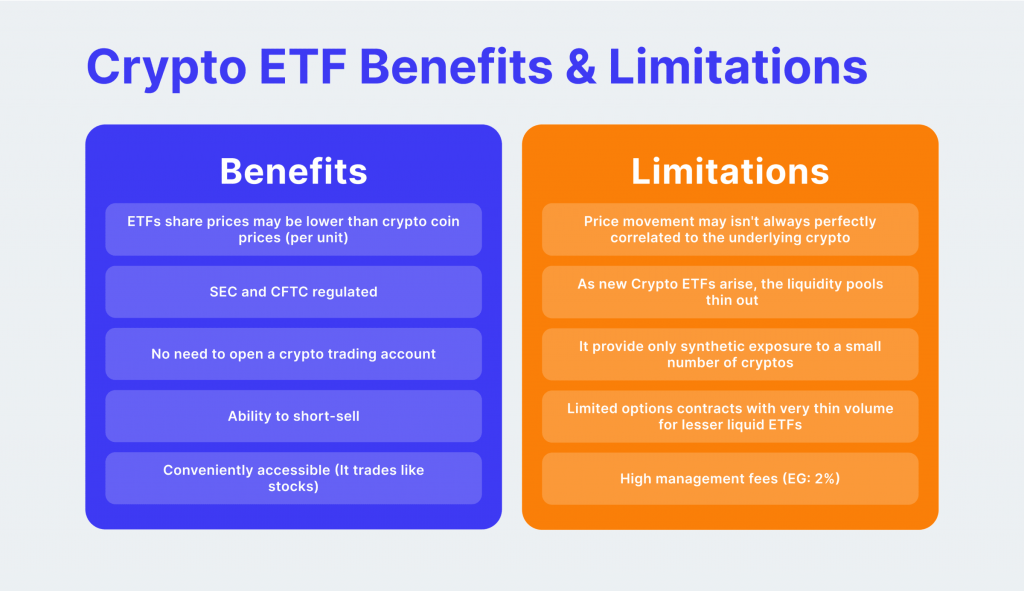
Regulatory Oversight and Transparency
Crypto ETFs benefit from robust regulatory oversight by entities such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). This oversight ensures that ETFs adhere to strict reporting and operational standards, providing investors with a higher level of transparency and protection. For example, the recent discussions around crypto ETF approvals highlight the importance of regulatory scrutiny in maintaining market integrity.
Ease of Access and Trading
One of the main advantages of crypto ETFs is their ease of access. Investors can buy and sell ETF shares through their regular brokerage accounts, just like they would with stocks. This convenience simplifies the process of gaining exposure to cryptocurrencies. Additionally, ETFs are listed on major stock exchanges, ensuring high liquidity and ease of trading.
Diversified Exposure
Crypto ETFs often provide exposure to a diversified portfolio of cryptocurrencies or related assets. This diversification helps mitigate the risk associated with investing in a single cryptocurrency. For instance, some of the best crypto ETFs hold a mix of Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other prominent cryptocurrencies, providing a balanced investment approach.
Lower Expense Ratios vs Other Types of Funds
ETFs typically have lower expense ratios than actively managed funds. This cost efficiency is passed on to investors, making ETFs an attractive option for those looking to minimise investment costs. For example, Bitcoin futures ETFs often have lower fees than mutual funds or hedge funds with similar exposure.
Key Advantages of Crypto ETPs
Broader Range of Investment Options
Crypto ETPs offer a broader range of investment options than ETFs. This includes exposure to not only cryptocurrencies but also related financial instruments such as debt securities, futures, and commodities. This flexibility allows investors to tailor their portfolios to their specific risk tolerance and investment goals.
Innovative Investment Strategies
ETPs can employ more innovative and complex investment strategies than ETFs. For instance, inverse ETPs allow investors to profit from declines in cryptocurrency prices, while leveraged ETPs amplify the returns (and risks) of the underlying assets. These strategies can provide significant opportunities for sophisticated investors looking to capitalise on market volatility.
Higher Liquidity
Some crypto ETPs, especially those that track widely traded cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, offer higher liquidity than individual cryptocurrencies. This higher liquidity can result in tighter bid-ask spreads and more efficient price discovery, benefiting investors by reducing trading costs and improving market access.
Accessibility for Retail Investors
ETPs are often designed to be accessible to a broader range of investors, including retail investors. This democratisation of access means that smaller investors can participate in the cryptocurrency market without needing to invest large sums of money or navigate the complexities of cryptocurrency exchanges.
Choosing Between Crypto ETFs and ETPs
The choice between a crypto ETF and an ETP depends on your individual investment strategy and risk tolerance. Here are some factors to consider:
Market Exposure: If you’re looking for direct exposure to the price movements of a specific cryptocurrency, a crypto ETF that holds the underlying asset might be a better fit.
Regulatory Oversight: Crypto ETFs are still a relatively new phenomenon, and regulations can vary depending on your location. On the other hand, ETPs have been around longer and may offer a more established financial industry regulatory authority.
Investment Objective: Are you seeking a passive investment that tracks the overall crypto market, or do you prefer an actively managed fund with a specific strategy? Both ETFs and ETPs can cater to different investment objectives.
Fast Fact
The first ETF was launched in Canada in 1990, which paved the way for the introduction of the first U.S. ETF, the SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust, in 1993. Designed to offer investors the diversification of a mutual fund with the flexibility of stock trading, ETFs took time before they started to grow rapidly in popularity.
Comparing Bitcoin ETPs and ETFs
When it comes to Bitcoin-specific investment options, both ETFs and ETPs offer unique benefits and considerations.
Bitcoin Exchange Traded Funds
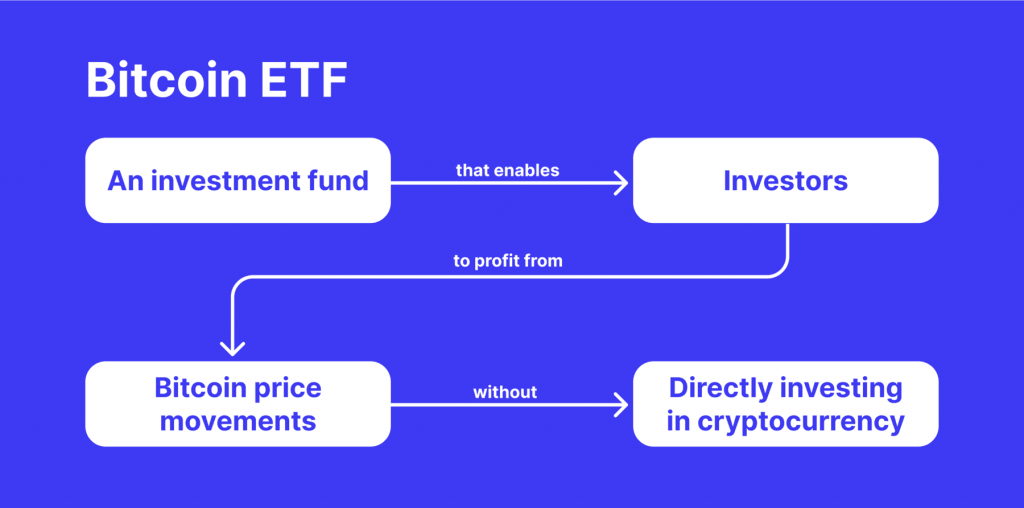
- Regulation: Bitcoin ETFs, such as those by prominent financial institutions like BlackRock, are subject to stringent regulatory approval processes.
- Simplicity: Bitcoin ETFs provide a straightforward way to gain exposure to Bitcoin’s price movements without the need to manage digital wallets or private keys.
- Market Impact: The approval of a spot Bitcoin ETF significantly impacts the market by increasing institutional and retail participation, potentially driving up demand and stabilising prices.
Bitcoin ETPs
- Variety: Bitcoin ETPs can include different types of products, such as ETNs and ETCs, which may have varying degrees of risk and return profiles.
- Innovation: Bitcoin ETPs often incorporate innovative features, such as leverage or inverse performance tracking, allowing investors to implement more complex trading strategies.
- Accessibility: Bitcoin ETPs might be more accessible in jurisdictions where ETFs have yet to be approved, providing an alternative way for investors to gain exposure to Bitcoin.
Comparing Ethereum ETPs and ETFs
As the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalisation, Ethereum has also seen significant interest from investors.
Ethereum ETFs

- Regulatory Framework: Similar to Bitcoin ETFs, Ethereum ETFs are subject to regulatory approval, ensuring a level of protection and transparency for investors.
- Diversified Holdings: Some Ethereum ETFs might include a mix of Ethereum and related assets, providing a diversified investment option.
Ethereum ETPs
- Flexibility: Ethereum ETPs can offer exposure to Ethereum through various structures, including futures and other derivatives, providing more flexibility in investment strategies.
- Innovation and Risk: Ethereum ETPs may introduce innovative features like leveraged returns or inverse performance, which can appeal to more risk-tolerant investors.
How to Trade ETFs and ETPs
Now, let’s look through the process of trading ETFs and ETPs.
Steps to Trade ETFs
- Open a Brokerage Account: Ensure the brokerage platform offers access to a wide range of ETFs, including crypto ETFs.
- Research: Use resources like the crypto ETF list to identify suitable ETFs based on your investment goals and risk tolerance.
- Place Orders: Buy or sell ETF shares through your brokerage account, just like trading stocks.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly review your ETF investments and adjust your portfolio as needed to align with your investment strategy.
Steps to Trade ETPs
- Understand the Product: Before trading, ensure you fully understand the specific type of ETP, its underlying assets, and its risk profile.
- Choose a Platform: Select a trading platform that offers a range of ETPs, including cryptocurrency ETPs.
- Execute Trades: Place buy or sell orders for ETPs, considering factors such as liquidity and market conditions.
- Risk Management: Protect your investments by employing risk management strategies, such as setting stop-loss orders.
Conclusion: The Future of Crypto ETFs and ETPs
The crypto market is constantly evolving, and regulations surrounding crypto ETFs and ETPs are likely to adapt alongside it. As the market develops and gains wider acceptance, we can expect to see a broader range of crypto ETFs and ETPs emerge, offering investors even more options to gain exposure to this dynamic asset class.
By understanding the differences between ETFs and ETPs and carefully considering your investment goals and risk tolerance, you can make an informed decision about whether these instruments are suitable for your portfolio. Remember, the crypto market is exciting but also carries inherent risks. Always conduct thorough research and invest cautiously.
FAQ
1. Is an ETF a private equity fund?
Private equity exchange-traded funds hold companies that can be financially complicated because they use leverage and are strongly transaction-oriented. However, they provide investors with exposure to private equity investments and can offer significant and attractive returns on investment.
2. Has ETH ETF been approved?
Ethereum ETF news: The US Securities and Exchange Commission on May 23 (2024) approved applications from Nasdaq, CBOE and NYSE to list ETFs tied to the price of ether, potentially paving the way for the products to begin trading later this year.
3. What is the Bitcoin ETF approval date?
Ten years after the first spot Bitcoin exchange-traded fund application was filed in the US, the SEC finally approved spot Bitcoin ETFs on January 10, 2024.
4. Which are the best crypto ETFs?
iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT), Bitwise Bitcoin ETF (BITB), Grayscale Bitcoin Trust ETF (GBTC), VanEck Ethereum Strategy ETF (EFUT), Global X Blockchain ETF (BKCH), Amplify Transformational Data Sharing ETF (BLOK), ProShares Ultra Bitcoin ETF (BITU) are some of the best crypto ETFs on the market today.
5. Can I buy an ETF for $1?
There are no restrictions on how often you can buy and sell stocks or ETFs. You can invest as little as $1 with fractional shares, there is no minimum investment, and you can execute trades throughout the day rather than waiting for the NAV to be calculated at the end of the trading day.