Private Keys vs Seed Phrase: Differences to Be Aware of
Imagine your crypto wallet as a digital repository that contains high-value funds. To get into this vault, you need a unique key that only you possess, granting you full control over every coin and token inside. But just like any precious item, there’s always the risk of losing it — misplacing the key or even stealing it.
That’s where a reliable backup plan comes into play, ensuring that even in the worst-case scenario, you can regain access to your wealth. This is achievable thanks to secret keys and seed phrases, making a basement for crypto security.
This article will explain the differences between private keys vs seed phrase.
Key Takeaways
- Secret encryption keys and seed phrases are two must-have items of crypto wallet operation.
- A private key controls your crypto tools, while a seed phrase serves as a recovery method for your wallet.
- Although both offer security, they do so in distinctly different ways.
What Is a Private Key?
A private key is critical information in digital tools and cryptos. It’s a long, unique, randomly generated string of alphanumeric characters that acts as a “password” for a digital wallet. Simply put, a private key is the only way to access, manage, and control the funds in a wallet.
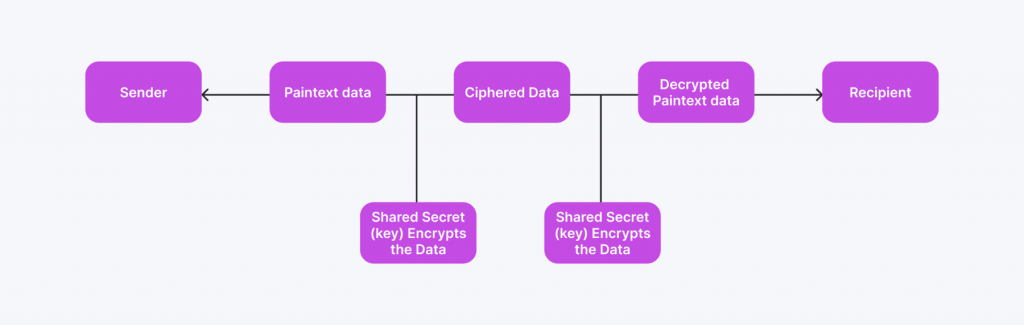
In cryptocurrency transactions, the private key is essential for authorizing transfers and verifying ownership of digital assets. It is paired with a corresponding public key derived from the private key and serves as the wallet address others can use to send funds. However, only the private key can unlock those funds and allow transactions.

The private key is designed to be kept entirely confidential. Unlike a traditional password or PIN, which can often be reset if forgotten, a private key cannot be recovered or replaced if it’s lost. If someone loses access to their private key, they lose ownership of the funds associated with that key, making it unrecoverable.
This irreversible loss highlights the importance of safeguarding private keys carefully, as misplacing them means permanently losing control over the assets tied to them.
On the other hand, if a private key is misappropriated or stolen, anyone possessing that key has full access to the wallet and can move or spend the funds without any barriers.
For many users, wallet interfaces and hardware devices have simplified private key management, allowing users to hold cryptocurrency without directly handling or seeing the private key itself.
Advanced users, however, sometimes choose to manage their private keys themselves, often storing them offline in secure places or with backup measures like hardware wallets.
Given the high stakes, most wallets employ encryption techniques and authentication schemes to preserve private keys. Still, it’s ultimately up to the user to keep these keys safe from unauthorized access.
Fast Fact
A seed phrase can regenerate an entire crypto wallet, including all its private keys, on any compatible device—making it the ultimate master backup in digital assets.
What is a Seed Phrase?
A seed phrase is a critical element in cryptocurrency and blockchain technology, serving as a user-friendly way to back up and restore access to a crypto wallet. Sometimes referred to as a resorption or retention pattern, a seed phrase is typically a sequence of 12 to 24 simple, randomly generated words.
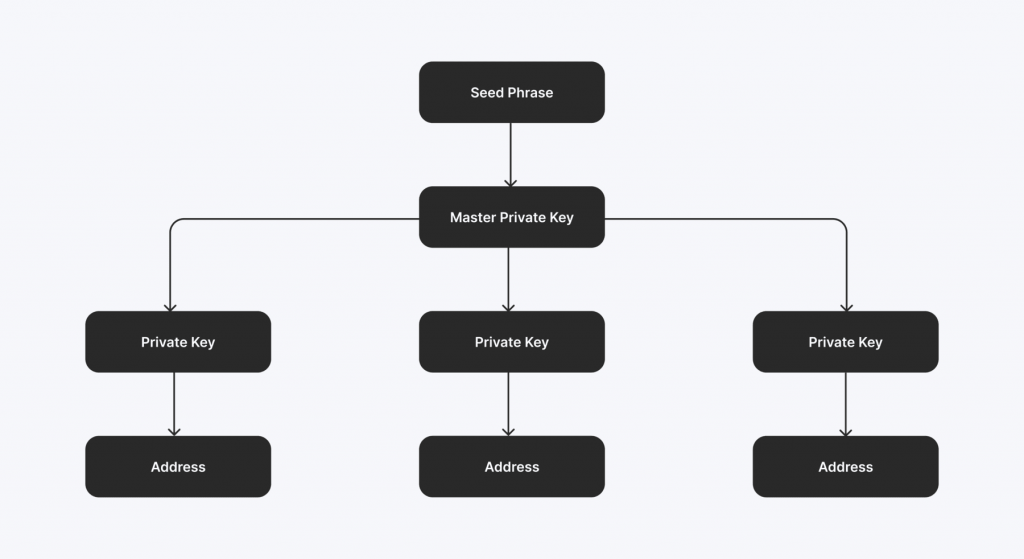
These words are selected from a specific list used by wallet software to create and regenerate the unique private keys that grant access to funds. The simplicity of these everyday words makes them far more accessible to remember or store than a complex private key, making seed phrases an accessible and effective backup tool.
The seed phrase is foundational because it allows users to recover their wallet on any compatible device, even if the original wallet is lost, damaged, or compromised. Keeping the seed phrase secure can recreate the entire wallet, including all associated private keys and assets.
This makes it invaluable for cryptocurrency users who need a reliable recovery method. However, a seed phrase like a private key must be strictly confidential.
Anyone with access to the seed phrase has complete authority over the wallet and its assets, just as if they had access to the private key itself.
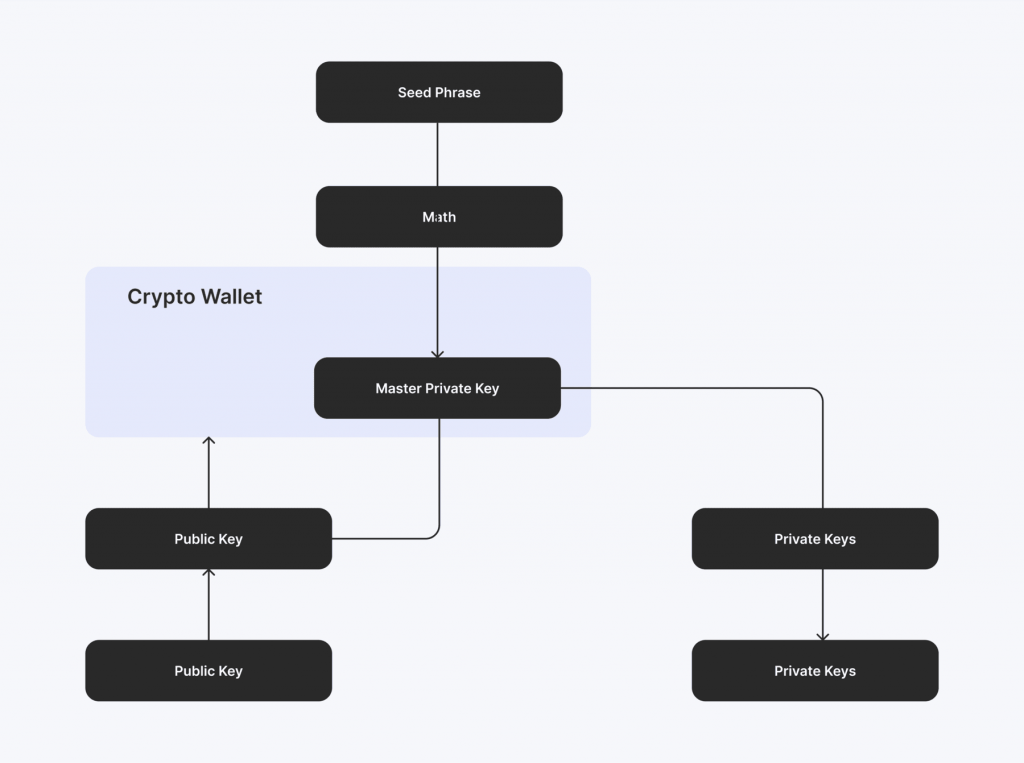
To ensure compatibility and security, most modern wallets use seed phrases that conform to industry standards like BIP39 (Bitcoin Improvement Proposal 39), which ensures that the words in the phrase can be universally interpreted across different wallets and platforms.
Cross-compatibility means users aren’t locked into a single wallet provider and can restore their wallets on other compatible wallets if needed.
However, this also means that the responsibility for securely storing the seed phrase falls entirely on the user, as wallet providers typically cannot recover a lost one.
Key Differences Between Private Keys vs Seed Phrase
Although both private keys and seed phrases provide security and safety for the wallet assets where they are used, their functionality and general purpose are slightly different. In particular, the main differences include.
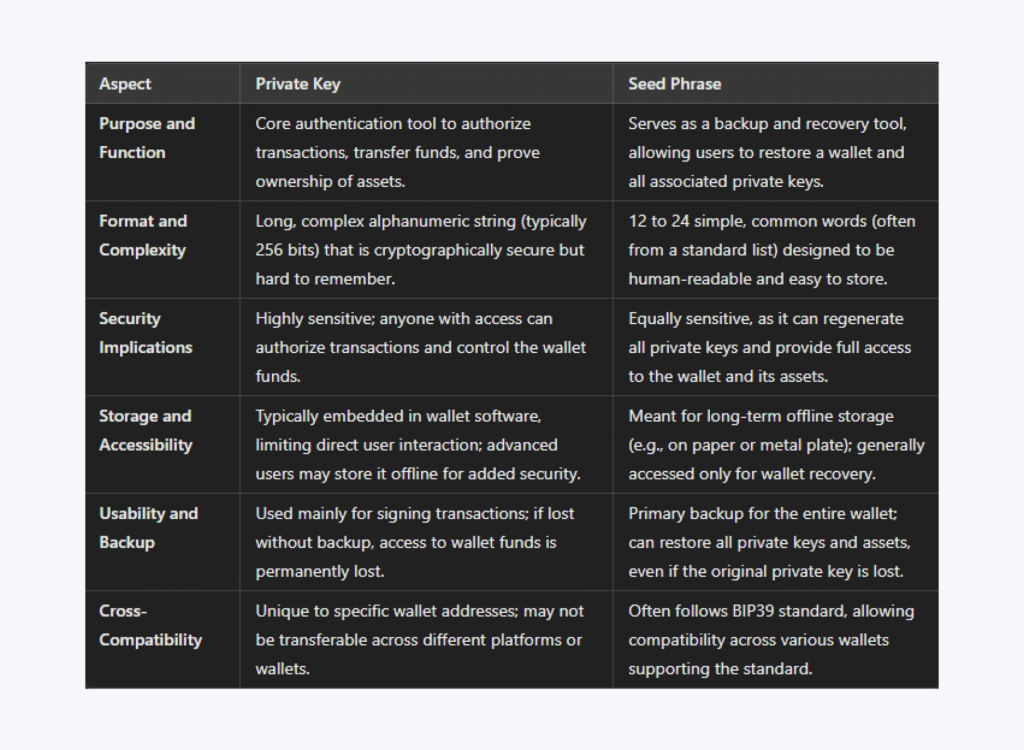
Purpose and Function
The private key is the core authentication mechanism for managing crypto assets. Each private key is integrated with a special public key, forming a cryptographic pair that allows users to access and control their funds securely. The private key lets users authorize transactions, transfer funds, and prove ownership by signing transactions cryptographically.
Once a transaction is signed with a private key, it’s broadcast to the blockchain, where it is verified and recorded. This way, private essential functions like a secure digital authentication code, unique to each wallet, grant sole access to a user’s funds.
The seed phrase is designed as a backup and recovery tool rather than a key used for daily transactions. When a wallet is initially created, it generates a seed phrase that serves as a root for all private keys within that wallet.
The seed phrase, therefore, acts as a “master backup” for the wallet and can be used to regenerate the wallet and all private keys associated with it if the original wallet is lost or damaged.
Notably, the seed phrase doesn’t directly engage with transactions or transfers; it is stored safely as a last-resort recovery tool. In the event of wallet loss, the seed phrase allows users to recover access on any compatible platform.
Format and Complexity
A private key is a long, complex alphanumeric string, typically 256 bits long, ensuring high levels of cryptographic security. This complexity is vital because it makes it extremely difficult for hackers to guess or brute-force the key.
Due to this length and randomness, a private key is not human-readable or memorable and is practically impossible for users to store mentally. As a result, private keys are often embedded within wallet software and managed by the wallet’s interface to reduce the risk of user error or accidental exposure.
The seed phrase, in contrast, is specifically designed to be human-readable and memorable. Consisting of 12 to 24 common words, often from a predetermined word list (such as BIP39’s 2048-word list), a seed phrase enables users to back up their wallets more practically.
Because it uses everyday words, the seed phrase is far easier to write down, store offline, and retrieve. This format allows for more secure and convenient management while still providing robust security through a process that transforms the phrase into the required cryptographic material to recreate private keys.
Security Implications
The private key is the most sensitive piece of information in a wallet, as it directly enables full control over all transactions. If someone gains access to the private key, they can authorize transactions without the owner’s consent, potentially emptying the wallet. For this reason, the private key is kept hidden by the wallet interface in most user-friendly wallets.
Users should avoid storing private keys in digital form, particularly in cloud storage or on internet-based devices, due to the risk of hacking, malware, or phishing attacks. Advanced security options, like hardware wallets, allow users to store private keys offline to minimize exposure.
Although the seed phrase is not used to sign transactions directly, it can regenerate all the private keys associated with a wallet. This makes it equally sensitive, as possessing the seed phrase effectively provides access to the entire wallet and all its funds.
Unlike private keys, which might be required for specific transactions, the seed phrase is generally stored and only accessed when necessary for wallet recovery.
However, because it gives full access, it should be stored securely in an offline location and protected from both theft and environmental damage (e.g., fire or water).
Storage and Accessibility
Private keys are usually embedded within the wallet software, which makes them accessible only when transactions are authorized. This approach reduces the need for users to interact directly with private keys and minimizes the chance of accidental exposure.
Some advanced users, however, may opt to store private keys offline (e.g., on paper or in a hardware wallet) to add an extra layer of security. For those who prefer even greater control, private keys can be stored on air-gapped (never connected to the internet) devices, but this approach requires advanced understanding and management.
The seed phrase is created explicitly for long-term storage and accessibility during recovers. Since it is only needed when setting up or restoring a wallet, it can be written down and stored offline, such as in a safe or vault, to prevent unauthorized access.
Many users take additional steps to secure their seed phrase, such as engraving it on a metal plate to protect it from physical damage. Importantly, storing the seed phrase on digital devices or in cloud storage is discouraged, as this can expose it to malware or online theft.
Usability and Backup
If a user loses their private key without having a backup, they lose entitlement to the funds in that wallet permanently, as there’s no way to regenerate or reset a private key. The private key’s usability is mainly in signing transactions, and for most users, it is something they never see directly, as wallet software often handles it.
Users who have backed up their private keys may choose to store them offline or in encrypted digital files. However, the seed phrase usually acts as the primary replica, so it can be recreated even if the private key is gone.
The seed phrase is explicitly created for backup and recovery, enabling users to restore their entire wallet on any compatible device or platform, including all private keys.
As it can recreate all private keys associated with the wallet, it is a critical backup that should be protected but is not typically used in everyday transactions.
This backup feature means that as long as the seed phrase is stored securely, users can always recover their wallet, even if they lose access to the original device or software.
Cross-Compatibility
Private keys are unique to specific wallets and addresses and may not be transferable across platforms. Some wallet providers use different protocols or formats for private keys, which can limit their portability.
In most cases, users must manage separate private keys for different wallet addresses and might need additional software to transfer funds across incompatible platforms.
Seed phrases are more flexible, particularly those following the BIP39 standard. A BIP39-compatible seed phrase can be used across various wallets that support this standard, allowing users to switch between compatible wallets without losing access to their funds.
This compatibility is beneficial in cases where users want to transfer assets from one wallet provider to another or restore access to their funds in the event of wallet software issues.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between secret keys and seed phrases is paramount for anyone involved in crypto. Both serve as vital components of crypto storage integrity but have different roles and as crypto adoption grows, so does the importance of safeguarding these keys.
With the irreversible nature of blockchain transactions, misplacing or exposing private keys or seed phrases can result in significant financial losses. Therefore, prioritizing dependable storage and proficiency in these tools are the foundations of responsible crypto management, giving users peace of mind and the ability to preserve their assets over the long term.
FAQ
What is a private decryption key in the crypto area?
A private key is a unique, randomly generated alphanumeric string that confers rights to and jurisdiction over crypto coins in a wallet.
What is a seed phrase?
A seed phrase, sometimes called a recuperative or recurrent word pattern, is a series of 12-24 common words used as a reassurance for a crypto wallet.
How do private keys and seed phrases differ in function?
A private key enables transaction monitoring and asset allocation, similar to a secured password. A seed pattern, however, serves as a backup and recovery tool.
Can I use my private key to recover my wallet?
No, a private key alone cannot fully recover a wallet. It only controls specific addresses within the wallet. You’ll need the seed phrase to completely restore a wallet (and all associated secure keys).
Why is a seed phrase easier to store than a private key?
A seed phrase consists of simple, everyday words, making it easier to write down, remember, and store securely.
Is it safe to store my seed phrase digitally?
It’s generally unsafe to store a seed phrase digitally, especially on internet-accessed devices, as it could be exposed to hacking or malware.