What Is a Hash in Blockchain? How Does it Protect Your Crypto Transfers?
The foundation of cryptocurrencies introduced advanced technologies that facilitate safe and sophisticated transactions. Blockchain operations are not managed by centralised authorities like banks or companies.
Instead, they occur systematically and within seconds using a complex coding system and hashing that safeguards data security and transfer.
Hashing is a key element in blockchain technology, driving and ensuring data integrity, especially when managing a massive dataset of information and transactions. Different hashing functions and algorithms work collectively to ensure the smooth operations of decentralised ecosystems and platforms.
Let’s explain in detail what is a hash in blockchain and how it contributes to data security.
Key Takeaways:
- Hashing is a major function in blockchain technology, allowing it to store and process transactions.
- Hashing entails converting textual inputs into useful information strings as output.
- The blockchain uses different hash functions to secure data and identify if information has been tampered with.
Understanding Hash
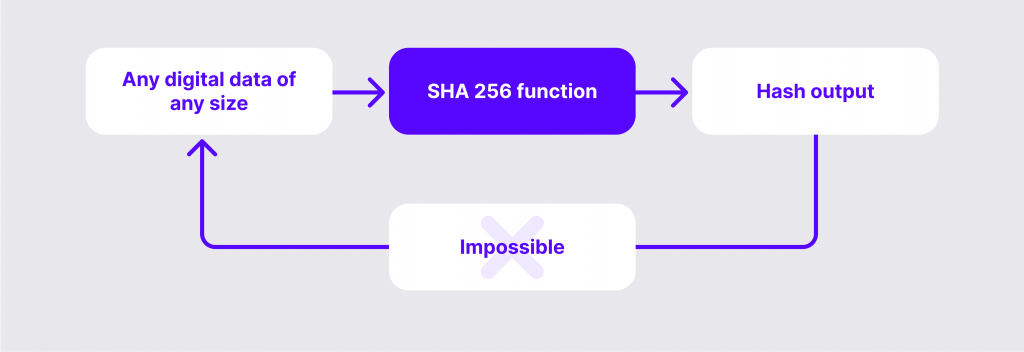
Hashing refers to the process of converting randomly inserted data such as text, images and numbers to fixed strings of data output that are understandable.
In other words, hashes act like identifiers for datasets, allowing systems to locate a broad range of information and documents using the unique hash ID.

How Does a Hash Work?
Hashing works like a message-passing protocol that uses input data to return outputs. There are different hash algorithms that determine how data is encrypted and secured, ensuring that processed information is not exposed.
When the original input data is inserted, it gets assigned a distinguished hash, which does not change regardless of how many changes happen to the associated information or the size of the stored data.
What is a Hash in Blockchain?
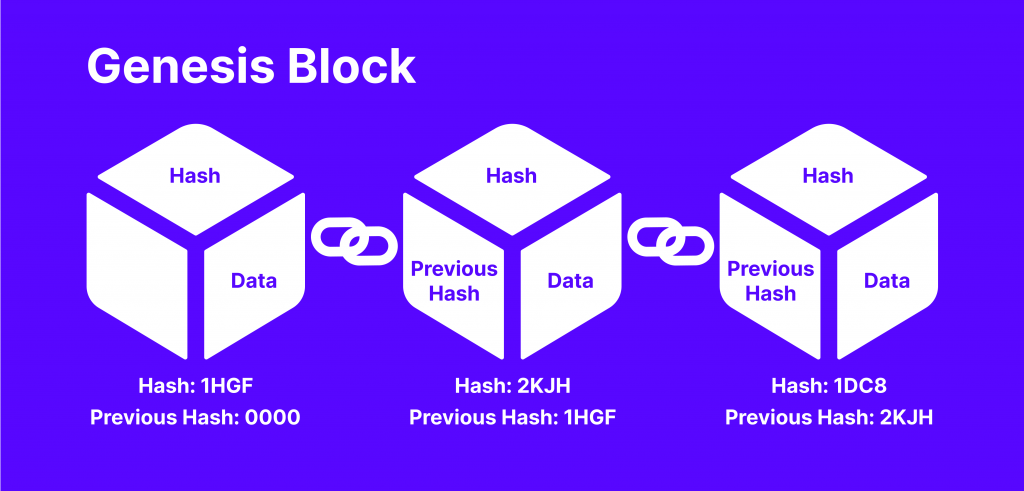
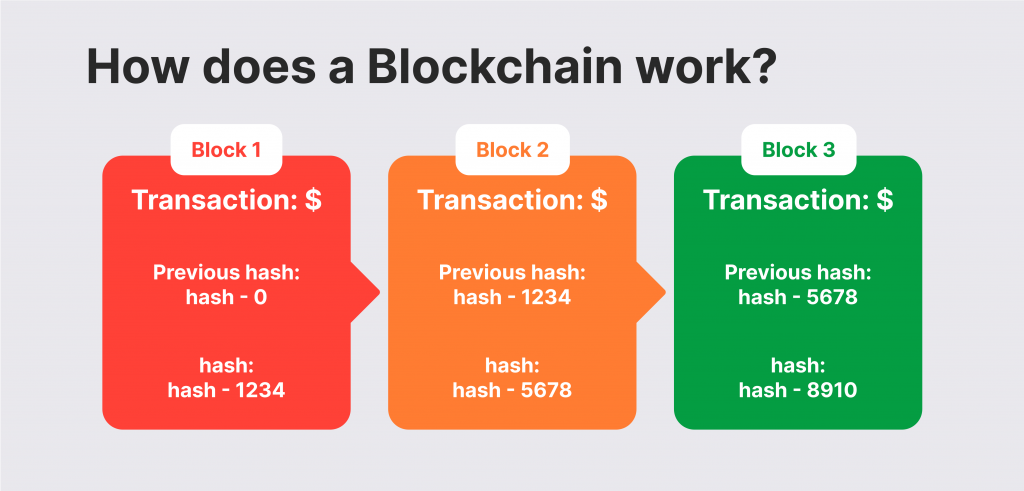
Blockchain technology relies on connecting (chaining) decentralised transactions subsequently as blocks of information with unique identifiers assigned to each one. Every verified transaction is added to a predecessor block and assigned a different ID or hash.
Cryptographic hash functions like fingerprints for digital information that facilitates the chaining of blocks together. Decentralised transactions are immutable, which means that they are irreversible and cannot be changed.
Cryptocurrency hashes carry the previous block header, which carries information like transaction number, timestamp, and the previous block’s hash value. Therefore, when a new block is added, its hash is compared with the previous one to show if the transaction was interfered with.
If any data in the blockchain gets leaked or changed, its hash number gets changed. This way, the system can uncover if a block was tampered with if its hash was changed.
Types of Hashes
Hashing functions work differently across blockchains, which deploy different algorithms that determine the length of data strings and fingerprint details. These various methods imply different ways to secure and pass information across networks and systems.
SHA-256
This type is one of the most common hash functions, which is used to create private and public keys that safeguard the transaction and wallet details. It checks if the block’s information has been altered or infiltrated.
MD5
The MD5 hash is a popular algorithm that converts values into hash output containing information strings of 128-bit, and these digital signatures consist of 32 characters. This hash type is used to generate public and private security keys.
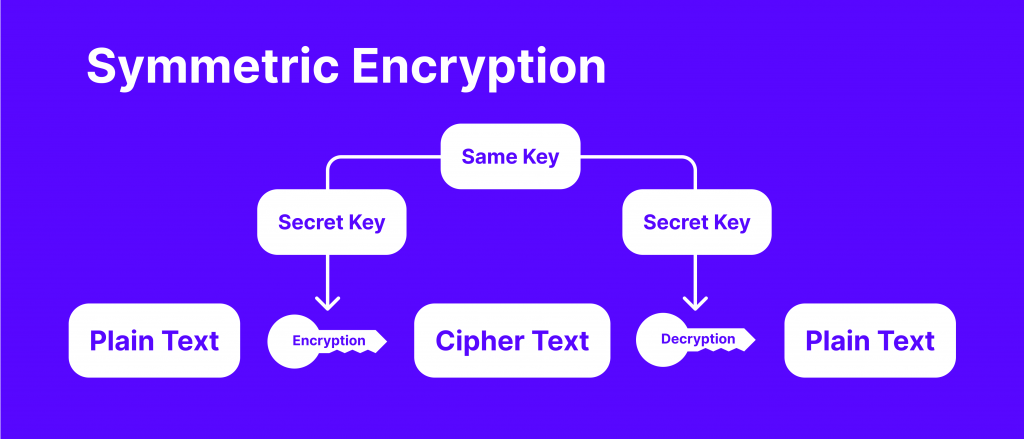
MD5 deploys a cryptographic function that authenticates the data integrity, ensuring that nothing has been tampered with or changed during the message transmission, making it one of the oldest and most used hash algorithms.
Tiger Algorithm
The Tiger algorithm is relatively newer and faster than MD5, with a higher capacity to create 192-bit long hashes. Besides its updated version, Tiger2, this approach is widely used in modern systems and servers.
The Tiger hashing system was created based on the Merkle-Damgard paradigm, pertaining to the resistant data design and structure with many security characteristics implemented in modern applications.
RIPEMD-160
RIPEMD-160 hash is also used to create public and private key pairs, with other functions to generate information output of 20 characters.
Additionally, this algorithm is used to ensure the authenticity of stored data and discover if any alteration happened to the chained blocks.
CRC32
CRC32 is also used to verify and confirm the authenticity of stored data and ensure no tampering has occurred. However, it follows a different paradigm.
The cyclic redundancy check (CRC) uses the error-detection approach in data validation to identify data changes, whether accidental or intentional, allowing systems to reveal if data leaks or exposure has happened.
How Does a Hash Help Secure Blockchain Technology?
Hashing is a key element of how crypto transfers work, which is a key element in data encryption, transmission and protection.
The decentralised network does not use a single hash to operate. Instead, it combines different hash algorithms to serve the function required better and promote a more rigid security system.
Hackers would need to breach every hash function on the nodes in order to hack the blockchain, which makes it technically impossible.
Cryptographic hashing has different use cases, allowing entities to store and transfer sensitive data and share it with a selected group of people. Therefore, hashes are used to safeguard information, validate the data integration and ensure that information was not changed using the original hash type.
SHA-256 Role in Blockchain Security
The SHA-256 hashing algorithm was developed in 1997 by the National Security Agency, and since then, it has been used to promote cybersecurity and ensure digital data protection.
This hashing protocol serves other purposes, including data verification and protection against alteration. This system can generate outputs of different sizes up to 512-bit, which makes it highly useful in different industries, including healthcare, military, finance, and insurance.
However, using this type alone to process big data can lead to delays because this function is relatively slow. Therefore, it is better used in combination with other hash functions like Whirlpool.
Use Cases of Hash Function in Cryptography
By now, we understand what is hash function and its role in promoting blockchain security and ensuring smooth operations. Let’s look at some practice use cases of hashing and how it is used.
Digital Fingerprinting
The cryptographic hash function facilitates the works of blockchain and its components, such as smart contracts, which encrypt and decrypt the transaction messages. Each cryptocurrency transfer is designated a special signature or fingerprint generated using hashing algorithms.
Then, transactions are decrypted before being passed over to validation nodes, which use hash functions to verify data. Finally, the transaction is passed to the receiving entity, which uses hashes to decrypt the message and realise the transferred funds.
Data Retrieval
Hashes are used to convert numbers and letters into useful information, designating stored data, such as patient records in healthcare or monetary funds in crypto transfers. Each hash function encodes the transaction and creates security keys to locate and interpret the data.
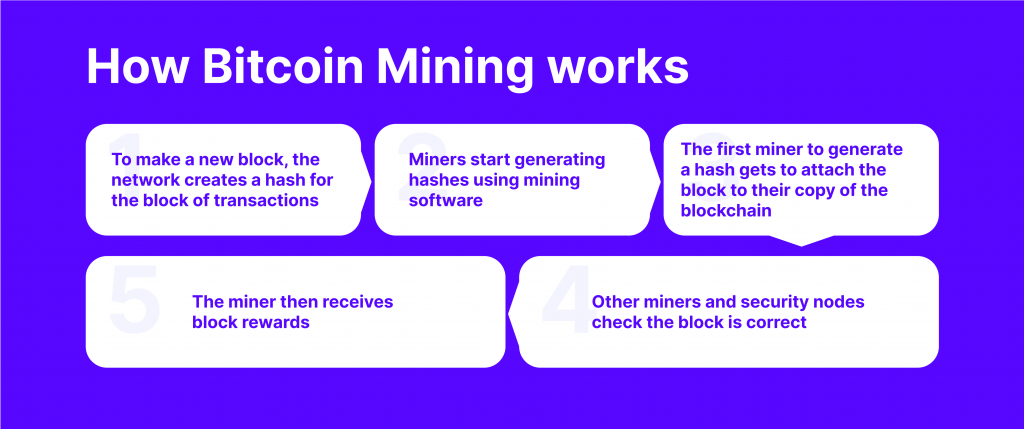
This feature is utilised in crypto mining, which involves solving complex mathematical equations to verify transactions.
The verification process entails comparing the hash values and ensuring that data was not tampered with. Thus, validating nodes verifies the information integrity and adds it as a new block to the blockchain.
Conclusion
Hash in blockchain is a key concept in cryptography, ensuring the working of decentralised economies and crypto transactions. This concept was created to protect digital platforms and online-stored information, which is highly used in decentralised economies and shared networks.
The hash function is used to encrypt and decrypt transactions and assign private keys to locate and retrieve data. The blockchain uses a combination of hash algorithms to promote data protection and ensure that data has not been altered or hacked.



