What is Crypto Vault, and How Does it Work?
In the crypto space — security is everything. With rising cyber concerns, hacks, and unauthorized access, storing your virtual assets in a safe vault crypto solution is no longer optional — it’s essential. A crypto vault acts like a digital safe deposit box, offering cold storage, multi-signature security, and withdrawal delays to safeguard your investments.
This article will explore how a crypto vault performs, its main types, key advantages, and how it differs from a crypto wallet, another crypto storage method.
Key Takeaways:
- Crypto vaults offer the highest level of security through cold storage, time-locked repayments, and multi-signature validation.
- Vaults are ideal for long-term investors and institutions, as they ensure funds remain protected from hacking, accidental transfers, and unauthorized access.
- Unlike wallets, vaults prioritize safety over convenience, making them perfect for securing large crypto holdings.
What Are Crypto Vaults?
A crypto vault is an advanced security solution designed to store cryptos with strengthened protection to prevent hacks, theft, and unauthorized access. In contrast to regular crypto wallets, which focus on accessibility, vaults prioritize long-term security by incorporating multiple security layers, such as cold storage, multi-signature authenticity, and time-delayed withdrawals. These features make crypto vaults ideal for investors, businesses, and institutions holding large amounts of digital assets.
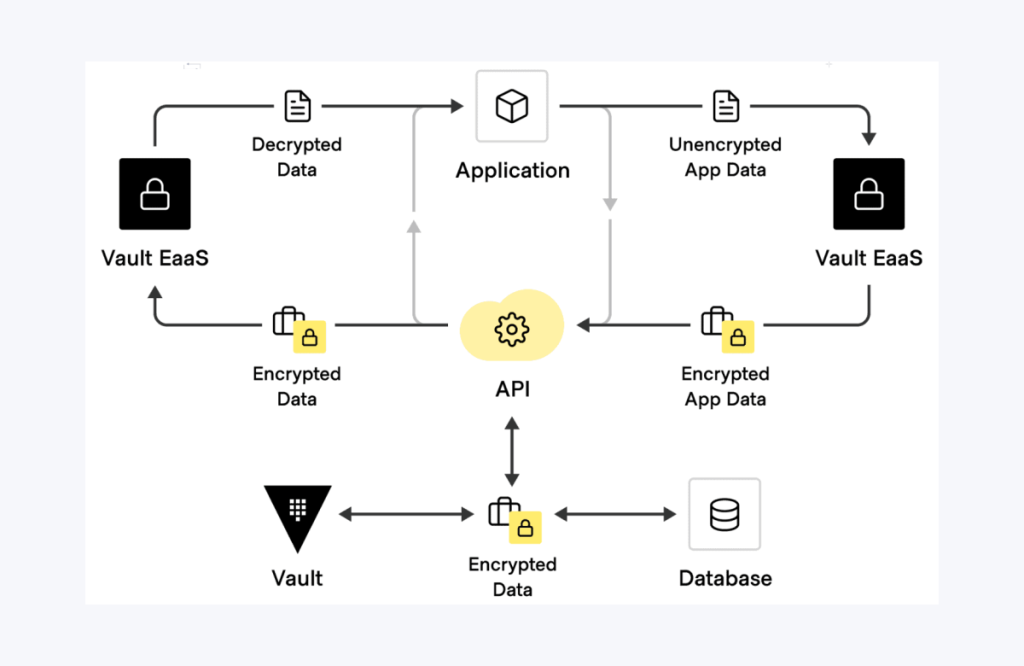
A crypto vault can be compared to a bank’s safety deposit box, as it offers a secure and long-lasting storage facility rather than immediate transaction access. In contrast to conventional crypto wallets, such as hot wallets that remain bound to the internet, vaults generally utilize cold storage techniques. This approach assures that exclusive keys are stored offline, which, importantly, diminishes the possibilities for cyber incidents.
Fast Fact:
The largest institutional crypto vaults, such as BitGo Custody and Coinbase Vault, hold billions of dollars in Bitcoin and other assets and provide insured protection for investors worldwide.
Main Types of Crypto Vaults
Crypto vaults come in various forms, each tailored to render maximum security and controlled access to digital assets. Depending on an investor’s needs, risk tolerance, and level of control, different vaults can be used to securely store virtual funds.
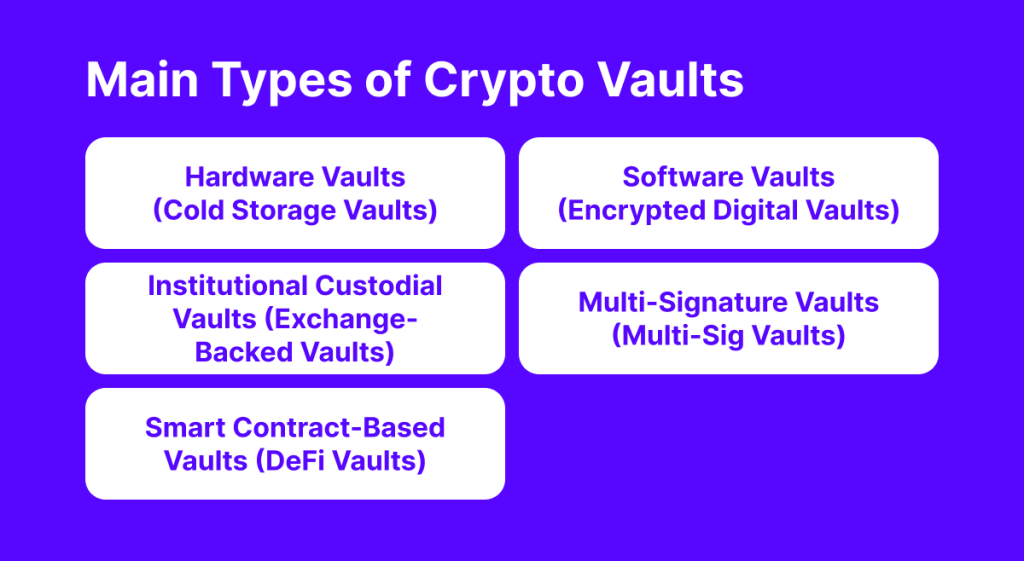
Here are the main categories of crypto vaults along with their distinct characteristics, benefits, and applications
Hardware Vaults (Cold Storage Vaults)
A hardware vault is a tangible device designed to keep discrete keys offline, safeguarding crypto assets from cyber threats, hacking efforts, and unauthorized access. By remaining disconnected from the internet, these vaults offer a robust defense against online attacks.
Private keys are stored on an encrypted USB-like device, such as Ledger, Trezor, or Coldcard. Transactions are signed offline, and only the signed transaction data is transferred to the blockchain through an internet-connected device. Some hardware vaults incorporate multi-signature encryption, requiring multiple approvals for fund access.
Hardware vaults are exceptionally secure, immune to malware, and give users full control over their assets. However, they come with the risk of physical damage or loss, and accessing funds requires possession of the device, which can be inconvenient for frequent operations.
Software Vaults (Encrypted Digital Vaults)
A software vault stores private keys in an encrypted digital format on a user’s device or a secure cloud-based storage system. This solution balances security and accessibility, implementing features like time-delayed withdrawals, MFA, and strong encryption protocols.
Private keys are secured within an encrypted file stored on a PC, smartphone, or external drive. Transactions require password authentication and sometimes additional verification steps to prevent unauthorized access. Some software vaults even have a self-destruct feature, which wipes stored keys if tampering is detected.
These vaults offer convenience over hardware vaults. They do not require a physical device and can be backed up using seed phrases or cloud storage. However, they remain vulnerable to cyber threats such as malware, phishing, or hacking.
Institutional Custodial Vaults (Exchange-Backed Vaults)
Institutional custodial vaults are professionally managed crypto storage services offered by exchanges, financial institutions, and security firms. They are primarily designed for large-scale investors, hedge funds, and enterprises that need a regulated and highly reputable storage solution.
These vaults store private keys in multi-layered cold storage systems, often distributed across different physical locations. Multi-signature authentication ensures that transactions require multiple approvals before processing. Some providers also offer insurance policies to protect against theft, loss, or hacking.
While these vaults provide institutional-grade security, they also require trust in third-party custodians, meaning investors do not have full control over their secret keys.
Multi-Signature Vaults (Multi-Sig Vaults)
Multi-signature (multi-sig) vaults require multiple private keys or approvals before transactions can be executed, adding another layer of discretion. This approach ensures that no single party can move funds alone, reducing risks associated with hacking and unauthorized access.
A typical multi-sig setup might require two out of three keys or three out of five to approve transactions. This makes it ideal for corporate treasury management, joint accounts, and family trusts, where shared control is necessary.
Multi-sig vaults prevent unauthorized withdrawals and protect against hacks. However, their setup can be complex, and disagreements between keyholders may temporarily lock funds.
Smart Contract-Based Vaults (DeFi Vaults)
Smart contract-based vaults operate entirely on the blockchain, using automated security protocols and predefined rules to control transactions. These vaults are popular in DeFi and provide full automation of security processes without relying on a third party.
Funds are stored in a DeFi vault, which is secured by smart contracts that enforce withdrawal limits, multi-signature requirements, and time delays. Some smart contract-based vaults also allow staking and yield farming, enabling users to earn passive income while securing their assets.
Since these vaults are fully decentralized, they eliminate the need for trusting a central authority. However, they come with risks such as smart contract vulnerabilities, where a bug in the code could be exploited. In addition, there is no customer support — users must manage their vault independently.
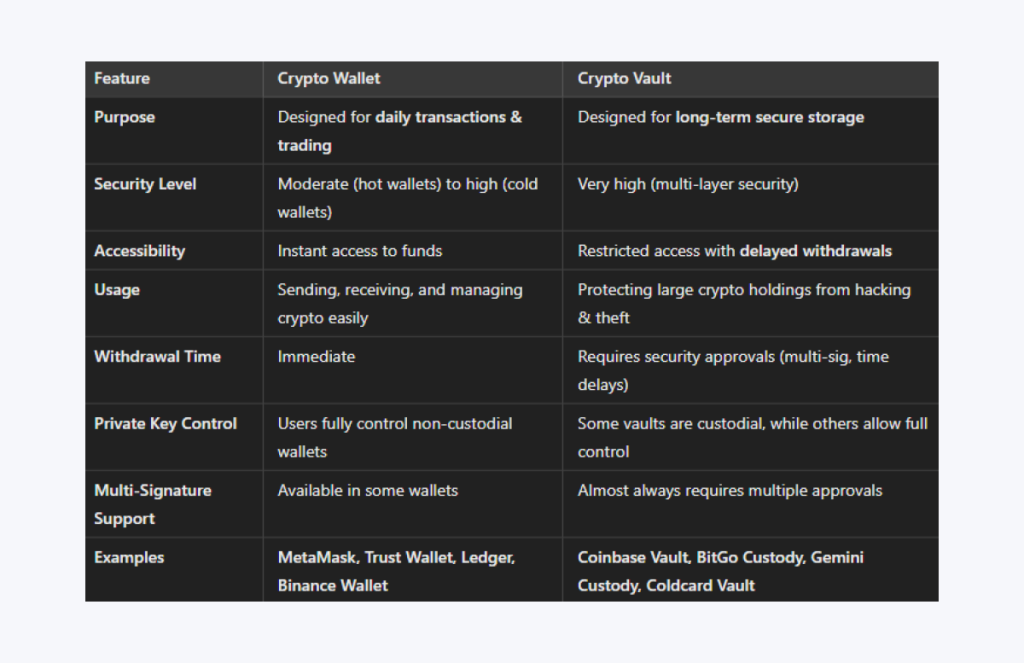
Key Differences Between a Crypto Wallet and a Crypto Vault
Cryptocurrency storage solutions fall into two main categories: wallets and vaults. While both serve as secure storage options for digital assets, they cater to different needs. Wallets prioritize accessibility and ease of operations, whereas vaults focus on maximum security and long-term storage.
Purpose
A crypto wallet is designed for users who frequently send, receive, and trade cryptocurrencies. It provides instant access to digital assets, making it ideal for traders, investors, and businesses handling daily transactions.
In contrast, a crypto vault is meant for those who prioritize security over convenience. It serves as a long-term storage solution for large crypto holdings and incorporates extra security layers to prevent unauthorized access and hacking, making it a good remedy for corporate investors and high-net-worth individuals.
For instance, traders using MetaMask or Binance Wallet benefit from quick access to their funds, whereas investors storing millions in Bitcoin would prefer the enhanced security of a Coinbase Vault or BitGo Custody.
Security Level
Security varies dramatically between wallets and vaults. Hot wallets (software-based, tied to the internet) offer moderate security but remain susceptible to cyberattacks. Cold wallets promise better protection, yet they are still more accessible than vaults.
Crypto vaults, on the other front, utilize multi-layer security measures, including cold storage, time-delayed repayments, and multi-signature authentication. These features make vaults significantly safer than standard wallets, eliminating most hacking risks.
A MetaMask hot wallet, for example, is more vulnerable to online threats than a Coldcard hardware vault, which operates entirely offline.
Accessibility
One of the primary differences is how users can access their funds. A wallet allows instant transactions, making it suitable for day-to-day trading and payments. Vaults, however, impose withdrawal restrictions, ensuring that funds cannot be moved immediately or without additional security approvals.
Some vaults require multi-factor authentication (MFA), administrator confirmations, or enforced withdrawal delays to prevent unauthorized access.
For example, Trust Wallet enables users to transfer funds instantly, while a Coinbase Vault imposes a 48-hour security hold on withdrawals, providing an added layer of security in case of suspicious activity.
Usage
Crypto wallets act as convenient tools for managing cryptos, countenancing users to store multiple collections and make quick transactions. This makes them ideal for traders, businesses, and everyday crypto users who need fluid access to funds.
Vaults function more like a bank’s safety deposit box, safeguarding large crypto holdings from potential theft or loss. By limiting accessibility and integrating security controls, vaults provide maximum protection for long-term investors and businesses handling institutional-grade crypto funds.
A business accepting Bitcoin payments would use a hot wallet like Binance Wallet for daily transactions, whereas an investment firm managing large Bitcoin reserves would store funds in a BitGo Custody vault for optimal security.
Withdrawal Time
Crypto wallets are designed for speed and efficiency, enabling users to move funds instantly. In contrast, vaults prioritize security over speed, requiring additional time-delayed approvals, multiple signatures, or administrative confirmations before withdrawals can be processed.
A MetaMask user can withdraw funds immediately, whereas a Coinbase Vault withdrawal might require a 48-hour delay, ensuring that transactions cannot be rushed or exploited.
Private Key Control
The ownership and control of private keys differ between wallets and vaults. A non-custodial wallet (e.g., Ledger, MetaMask) gives users full supervision over their private keys, meaning they alone are responsible for securing their funds. However, if the key is lost, the funds are irrecoverable.
Vaults can be custodial or self-custodial, depending on their type. Some, like Coinbase Vault or BitGo Custody, store private keys on behalf of users while implementing strict access controls.
Others allow users to maintain full control but incorporate extra layers of security. For example, a Ledger wallet user controls their own keys, while a Coinbase Vault user relies on Coinbase’s security infrastructure but benefits from additional protections.
Multi-Signature Support
Wallets may offer multi-signature (multi-sig) security, but it is often optional. Multi-sig requires multiple private key approvals before a transaction is processed, reducing the risk of unauthorized withdrawals. Vaults almost always include multi-signature authentication as a core feature, making unauthorized access significantly more difficult.
For instance, a MetaMask wallet typically requires only one private key for transactions, whereas a BitGo Custody vault may require approvals from two or more trusted parties before releasing funds.
Examples of Crypto Wallets vs. Crypto Vaults
Popular crypto wallets include MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Ledger, Binance Wallet, and Exodus, designed for accessibility and ease of use. Crypto vaults, such as Coinbase Vault, BitGo Custody, Gemini Custody, and Coldcard Vault, offer institutional-grade security and restricted access.
A trader using MetaMask benefits from fast and easy Ethereum transactions, whereas a long-term Bitcoin holder using Coldcard Vault ensures their assets are stored with maximum protection against hacks and loss.
Advantages of Crypto Vaults
Crypto vaults offer unparalleled security, control, and risk mitigation, making them preferred for long-lasting storage and institutional-grade asset protection. Unlike traditional wallets, vaults incorporate multi-layered security features that safeguard digital assets from hacking, unauthorized withdrawals, and accidental transactions.
Here is the outline of the main advantages of utilizing a crypto vault.
Maximum Security Against Hacking and Cyber Threats
A major concern in crypto storage is exposure to hacking, phishing attacks, and virus infections. Hot wallets remain integral to the internet, making them susceptible to cyberattacks. In contrast, crypto vaults use cold storage, assuring confidential keys and sensitive data are never online.
Additionally, vaults employ multi-layer encryption, firewalls, and offline signing mechanisms, preventing unauthorized access even in the event of a cyberattack. Hardware vaults like Coldcard remain completely offline and require physical authentication, making them significantly more secure than online wallets like MetaMask.
Protection Against Unauthorised Withdrawals
Vaults add extra layers of security to prevent unauthorized fund transfers. Unlike regular wallets, where transactions can be executed instantly, vaults implement time-locked withdrawals, multi-signature authentication, and administrator approvals.
With time-locked withdrawals, any transaction request must wait 24–48 hours before execution, giving users time to cancel unauthorized or suspicious activity. Multi-signature vaults require multiple approvals before transactions are processed, ensuring that no single individual can access funds alone. Institutional users can also set custom withdrawal policies, reducing the risk of internal fraud.
For example, Coinbase Vault delays withdrawals for 48 hours, allowing account holders to review and cancel any unauthorized activity before the transaction is finalized.
Suitable for Long-Lasting Storage and Investment Security
For investors and institutions holding large amounts of cryptocurrency, vaults act as secure, long-term storage solutions, preventing unauthorized or impulsive access. Unlike hot wallets, designed for frequent orders, vaults function as crypto savings accounts, ensuring that assets remain untouched until needed.
Long-term investors, institutional crypto holders, and businesses securing digital reserves benefit from vaults’ highly restricted access and advanced security layers. For example, an investment firm storing $100 million in Bitcoin would rely on a BitGo Custody Vault rather than a standard wallet to ensure compliance and maximum security.
Multi-Signature Security for Extra Protection
A major advantage of vaults is their multi-signature authentication system, which requires multiple approvals before funds can be moved. Unlike standard wallets, which often rely on a single private key, vaults require two or more trusted parties to sign off on transactions, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
This feature is particularly useful for businesses, investment groups, and family trusts, where multiple stakeholders manage a single vault. For instance, a company using a BitGo multi-signature vault may require approvals from three executives before a withdrawal is processed, preventing unauthorized transactions and increasing corporate security.
Protection Against Impulsive or Accidental Transactions
Vaults eliminate the risk of accidental transfers or impulsive withdrawals by enforcing strict approval processes and time delays. In standard wallets, funds can be sent immediately, sometimes to the wrong address or without double-checking security protocols.
By requiring administrative approvals and enforced waiting periods, vaults help institutional investors, businesses, and individual users avoid mistakes that could lead to financial loss. For example, a CEO managing corporate reserves in a Gemini Custody Vault cannot withdraw funds without CFO approval, preventing unauthorized transactions.
Reduces Third-Party Risk (Self-Custodial Options Available)
Unlike custodial wallets, where exchanges control private keys, many vaults allow for self-custody, giving users full control over their assets. This removes dependence on third parties and eliminates risks associated with exchange failures, insolvencies, or regulatory seizures.
For those preferring institutional security, custodial vaults like BitGo Custody, Gemini Custody, and Coinbase Vault provide insurance-backed storage with professional oversight. On the other hand, a private investor using a Coldcard Vault retains full ownership of their Bitcoin, ensuring that no external party has access to their funds.
Insurance Coverage for Institutional Vaults
Institutional-grade crypto vaults often include insurance policies that protect against theft, fraud, or loss, providing some extra discretion for businesses, hedge funds, and high-net-worth investors.
Many of these vaults comply with financial regulations, undergo regular audits, and offer coverage in the event of security breaches. For example, BitGo Custody provides up to $250 million in insurance coverage, ensuring added protection regarding cyber threats and fraudulent activity.
Back-up and Preservation Options for Added Safety
One of the major risks in crypto storage is the permanent exclusion of access due to misplaced private keys. Unlike wallets, which can become irretrievable if a user loses their recovery phrase, vaults offer multiple data backup and recovery utilities, assuring funds can be restored even in worst-case scenarios.
Vaults incorporate encrypted backups, multi-signature redundancies, and institutional-grade disaster recovery protocols. For example, in a multi-sig vault with three keyholders, the funds can still be accessed securely even if one key is lost.
Regulatory Assessments for Institutions and Businesses
Compliance with financial regulations and security standards is essential for enterprises handling large-scale crypto assets. Vaults designed for institutional use, such as Gemini Custody and BitGo, operate under strict regulatory frameworks, ensuring businesses can securely store and manage funds while adhering to legal and financial guidelines.
Institutional vaults provide auditable security measures, adherence to anti-money laundering (AML) regulations, and enterprise-grade risk management solutions, making them trusted by hedge funds, exchanges, and financial institutions. Using a Gemini Custody Vault, a crypto hedge fund can ensure full regulatory compliance while securing client assets.
Conclusion
A crypto vault is an ultimate safeguard for investors who prioritize reliability over convenience. Whether you’re securing Bitcoin, Ethereum, or other digital assets, a vault offers multi-layered hedges to shield against hacks, unauthorized withdrawals, and accidental transactions.
For long-term investors, businesses, and institutions, selecting the right crypto vault can mean the distinction between losing everything to cyberattacks and keeping your investments safe for years.
FAQ:
What is a crypto vault, and how does it operate?
A crypto vault is a high-security storage system for virtual capital that stipulates cold custody, multi-signature confirmation, and time-locked withdrawals to prevent unauthorized access.
Crypto vault vs wallet: What’s the difference?
A wallet allows instant transactions, while a vault prioritizes security and restricted access with payout delays and multi-factor proof of ownership.
Is Coinbase Vault a good option for securing crypto?
Yes, Coinbase Vault provides multi-signature precautions and time-delayed withdrawals, making it one of the best crypto vaults for institutional and retail investors.
Are crypto vaults safe against hacking?
Yes! Vaults use cold storage, multi-sig authentication, and secret codes to protect virtual funds, making them far more reliable than hot wallets.
Who should use a crypto vault?
Long-term investors, businesses, and institutions looking for maximum integrity and protection related to unauthorized transactions and cyber threats.