What is Payment Tokenization, And How Does It Work?
In an era where digital transactions dominate, security concerns around payment fraud and data breaches have skyrocketed. Payment tokenization has emerged as a game-changing security measure, replacing sensitive payment details with randomly generated tokens to prevent cyber threats.
Businesses worldwide are adopting tokenization from e-commerce to mobile payments to ensure secure, seamless, and compliant transactions. But how does payment network tokenization work, and what does the future hold?
Key Takeaways:
- Payment tokenization updates sensitive payment data with unique tokens, ensuring safer transactions.
- Businesses use tokenization in e-commerce, digital wallets, and POS systems to protect consumer data.
- Future advancements in tokenization will integrate blockchain, AI security, and DeFi solutions.
What is Payment Tokenization?
Payment tokenization is a security process that modifies sensitive payment information, such as credit card numbers, with a unique, randomly generated token. This token acts as a stand-in for the original data, allowing transactions to be processed without exposing actual financial details.
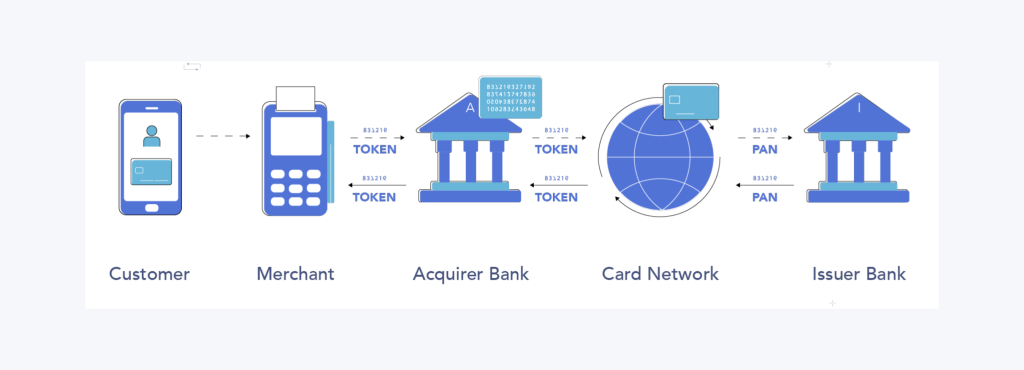
Unlike encryption, which transforms data into a coded format that can be reversed with a key, tokenization completely removes sensitive information from the transaction environment, ensuring that even if a hacker intercepts the token, it is useless without the corresponding tokenization system.
The primary purpose of payment tokenization is to enhance security in digital transactions. When a customer makes a purchase online, in-store, or via a mobile payment app, their credit or debit card details are replaced with a token before being transmitted for processing.
The token itself has no meaningful value outside the specific transaction or system it uses. Stolen tokens cannot be used to make unauthorized purchases, significantly reducing the risk of fraud and data breaches.
Fast Fact:
By 2030, major payment networks aim to eliminate manual card entry using tokenization, making digital transactions faster and more secure.
How Does Payment Tokenisation Work?
Payment tokenization alternates sensitive payment data with a secure, randomly generated token, ensuring transactions are processed safely without exposing actual card details. The process involves several key steps to protect financial information and minimize fraud risks.
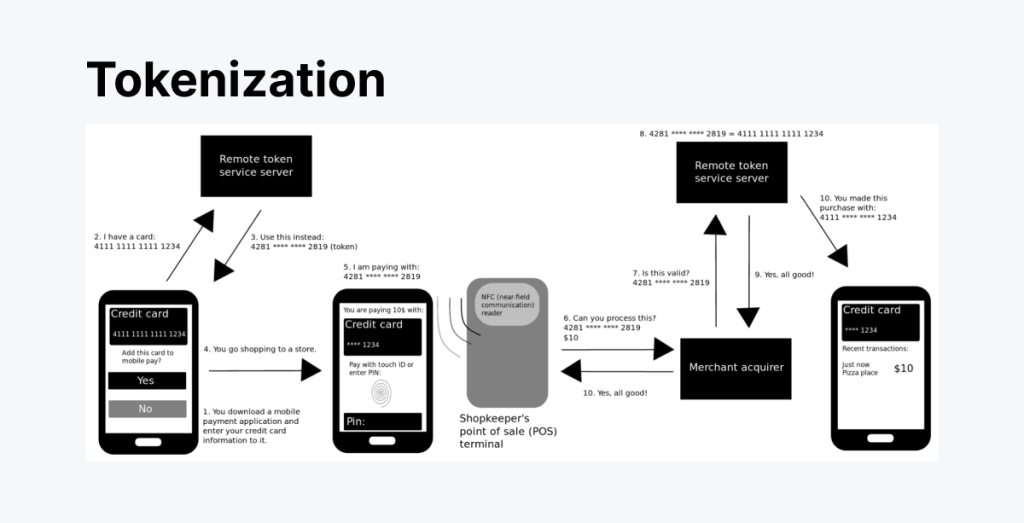
Initiating the Transaction
The process begins when a customer initiates a transaction by entering their payment details, including their name, card number, expiration date, and CVV.
Whether the payment is made online, in-store, or via a mobile wallet, the system detects the need to secure this sensitive data before proceeding. The entered payment details are then sent to a tokenization system, typically managed by a payment processor or a specialized service provider.
Generating the Token
The tokenization system generates a unique token, a randomly created sequence of numbers and characters. This token refers to the original payment data but has no value outside the system that created it.
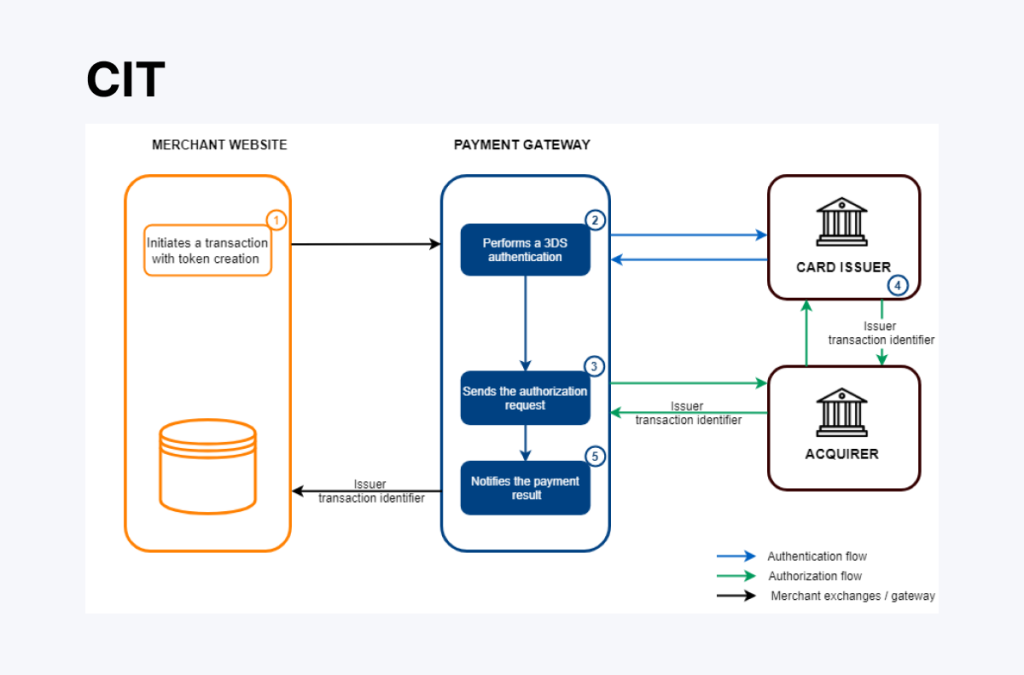
It cannot be reversed or decoded to retrieve the original card information. For example, a card number like 5123 4567 8912 3456 may be replaced with a token such as TKN-8792-ABCD-4501.
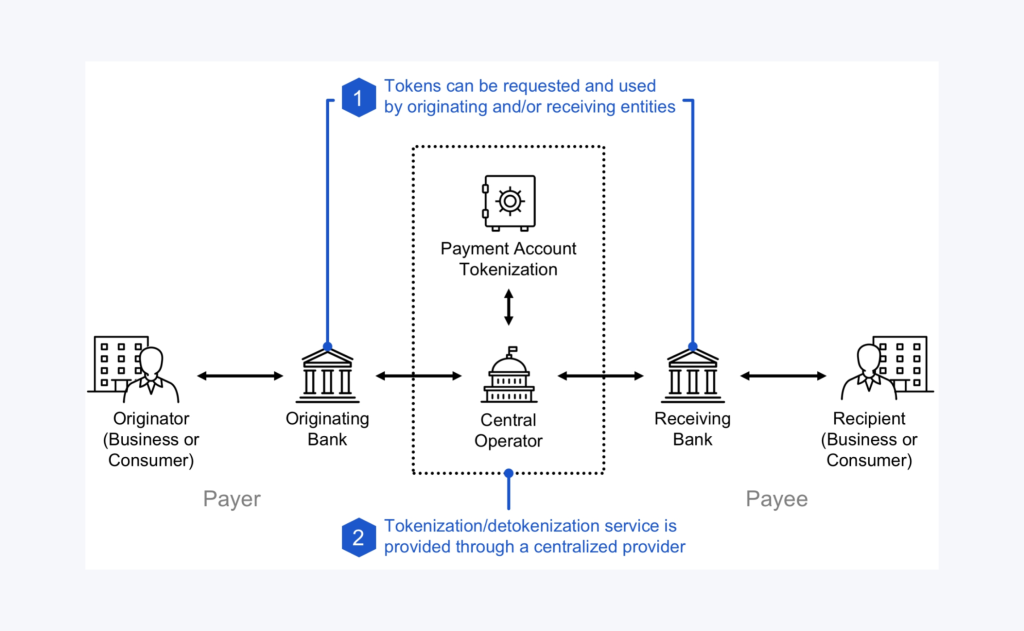
Storing the Token Securely
Once created, the token is stored in the merchant’s system instead of the actual card details. The original card data is securely kept in a token vault, protected storage managed by the tokenisation provider. Only authorized systems can access this vault when needed, such as for transaction processing or refunds.
Processing the Payment
When the payment is processed, the merchant sends the token, rather than the actual card information, to the payment processor or acquiring bank for authorization. The processor matches the token with the stored payment details and forwards the information required to the card network (such as Visa or Mastercard).
The issuing bank then verifies the transaction and either approves or declines it. If approved, the authorization is sent back through the payment network, allowing the merchant to complete the transaction.
Completing the Transaction
Finally, the customer receives a payment confirmation, and the business processes the transaction without handling or storing real card data. This ensures a higher level of security, prevents fraud, and reduces the risk of data breaches. Tokenization plays a critical role in modern payment security by safeguarding sensitive financial information at every transaction step.
Practical Applications of Payment Tokenisation
Payment tokenization has become a cornerstone of secure digital transactions, revolutionizing industries’ handling of sensitive financial data. By replacing real payment details with unique tokens, businesses can minimize fraud risks, enhance customer trust, and comply with regulatory standards. From e-commerce to mobile wallets and beyond, tokenization shapes the future of safe and seamless financial transactions.
Here are the most impactful applications across various industries.
E-Commerce Transactions
In online shopping, tokenization combines actual card details with a unique token, preventing merchants from storing sensitive information. This reduces the risk of data breaches and ensures compliance with PCI DSS regulations.
E-commerce platforms like Amazon and Shopify use tokenization for secure one-click purchases, providing a seamless checkout experience while protecting customer data from hackers.
Mobile Payments and Digital Wallets
Mobile wallets such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay rely on tokenization to secure transactions. When a user adds a card to a digital wallet, the system generates a unique, device-specific token.
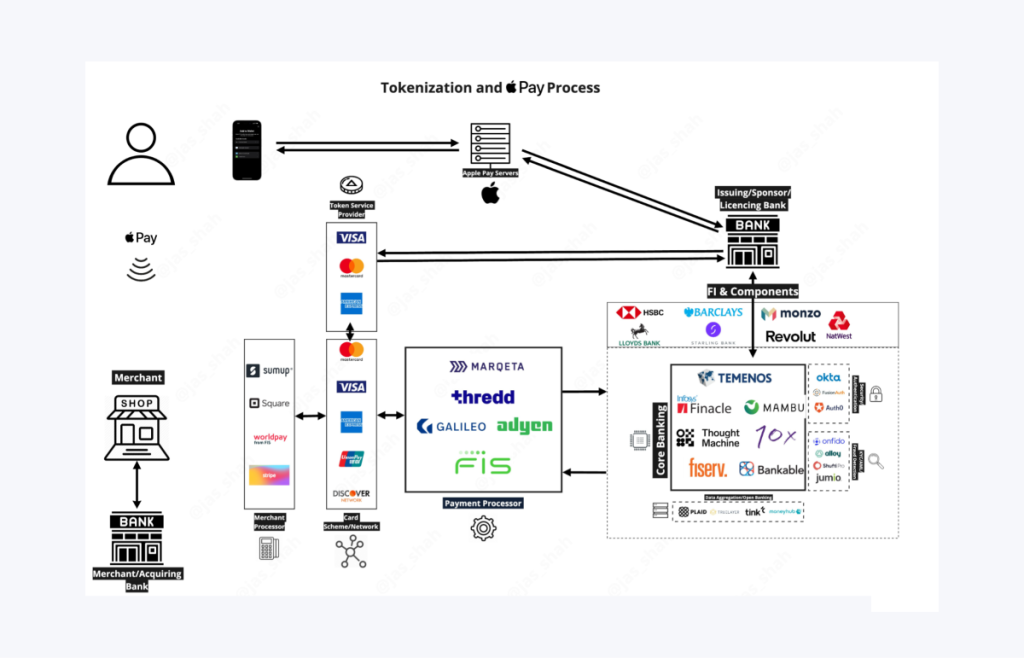
This ensures that the real card details remain protected even if the phone is lost or stolen. Additionally, each transaction generates a new token, reducing fraud risk, particularly in contactless NFC payments.
Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems
Retailers like Walmart and Target implement tokenization in their POS systems to protect customer payment information. Instead of transmitting real card data, the system exchanges it with a token, reducing the risk of fraud.
Hackers cannot access usable card details even if a POS system is compromised. This also helps businesses meet compliance standards while securing in-store transactions.
Subscription-Based Services and Recurring Billing
Platforms like Netflix and Spotify use tokenization to store customer payment details securely for recurring payments. Instead of keeping actual credit card numbers, tokens are stored for future billing cycles. This prevents unauthorized access to financial information while simplifying PCI DSS compliance.
In-App Payments
Apps that facilitate transactions, such as Uber Eats and DoorDash, use tokenization to protect user payment details. Tokenization ensures that apps do not store sensitive financial data while allowing seamless checkout experiences. This security measure particularly benefits high-volume mobile commerce transactions, reducing fraud risks.
Travel and Hospitality Industry
Hotels, airlines, and car rental services use tokenization to safeguard payment details during bookings and checkouts. This prevents unauthorized access to sensitive financial data, reducing fraud risks while ensuring compliance with data protection regulations. Platforms like Booking.com utilize tokenization to protect customer payments, both online and in person.
Healthcare and Insurance Payments
Hospitals, healthcare providers, and insurance companies use tokenization to secure payments for medical services and premiums. This method protects patient and financial data while ensuring compliance with HIPAA regulations. Patients making payments via online portals benefit from enhanced security, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain-Based Payments
Tokenization is widely used in blockchain transactions, where real-world assets such as fiat currencies, stocks, or digital assets are replaced with secure tokens.
This enhances security, prevents fraud, and enables fast and secure peer-to-peer payments. Decentralized finance platforms like Ethereum rely on tokenization for asset representation, providing users with safer and more efficient trading experiences.
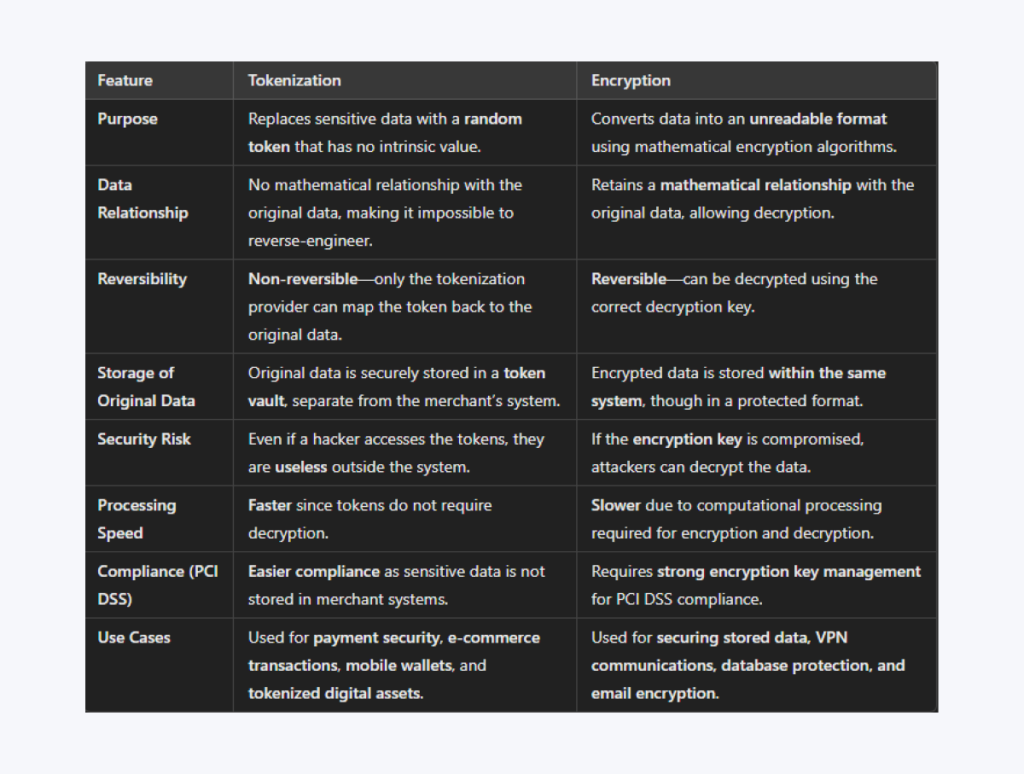
Tokenization and Encryption — Pivotal Differences and Examples
Both tokenization and encryption are essential security technologies for protecting sensitive data, particularly in financial transactions, data storage, and secure communications. While they share the common goal of securing information, they differ significantly in their functions, use cases, and security implications.
Below is a complete breakdown of their key differences.
Purpose
Tokenization switches out sensitive data, such as credit card numbers or personally identifiable information, with a randomly generated token with no intrinsic value. The real data is stored securely in a token vault, ensuring that businesses never directly handle or retain payment details.
Encryption, on the other hand, converts data into an unreadable format using complex mathematical algorithms. The encrypted data, known as ciphertext, can only be deciphered with the correct decryption key, making it secure for transmission and storage.
For example, a tokenized credit card number is useless outside the specific merchant’s system, whereas an encrypted credit card number can still be decrypted if the encryption key is compromised.
Data Relationship
A token has no mathematical relationship with the original data, making it impossible to reverse-engineer. This makes tokenization highly secure, as hackers cannot reconstruct the original data from a stolen token.
In contrast, encrypted data retains a mathematical relationship with the original data, meaning that if an encryption algorithm and its key are exposed, the original data can be decrypted.
For instance, a tokenized credit card number stored in an online shopping system cannot be converted to a real card number except by the authorized payment processor. However, encrypted customer data stored in a database could be decrypted if the encryption key is stolen.
Reversibility
Tokenization is non-reversible unless access to the secure token vault is granted. Only authorized systems can match a token with the original data, ensuring that even if a hacker steals a token, they cannot retrieve real payment details.
Encryption, however, is reversible. Data can be decrypted back into its original form using the correct decryption key. If the encryption key is stolen, however, the data is no longer secure.
If a cybercriminal gains access to tokenized credit card data, they cannot retrieve the real card numbers. However, they can quickly recover the original data by accessing an encrypted file with its decryption key.
Storage of Original Data
With tokenization, the original data is stored in a secure token vault, separate from the system that handles transactions or customer interactions. This eliminates the need for businesses to store sensitive payment information within their own databases.
Encryption typically stores encrypted data within the same system but in a protected format. While the data remains unreadable without the decryption key, its presence within the system increases the risk if compromised.
For example, in an e-commerce store, tokenized credit card numbers are stored in an external token vault, while encrypted customer addresses are stored within the company’s internal database.
Security Risk
Even if a hacker breaches a database containing tokens, they cannot use them outside the specific system where they were generated. Tokens are worthless outside the system unless the token vault is also compromised.
Encryption, however, carries the risk of key management — if the encryption key is stolen or leaked, all encrypted data can be decrypted, making it vulnerable to security breaches.
Hackers who breach a tokenized payment system will only find meaningless tokens that cannot be used to extract financial data. In contrast, hackers can access all stored payment details if they breach a system with encrypted payment data and steal the decryption key.
Processing Speed
Tokenization is generally faster because it does not require complex cryptographic computations. It simply overlays data with a token and retrieves the original information only when needed.
Encryption, in contrast, is slower because it requires computational power to decrypt and encrypt data. Decryption is necessary every time encrypted data is used, adding to processing time.
For example, tokenized payments are processed faster in high-volume transactions because they do not require decryption. However, encrypted payment data requires additional time for decryption before the transaction can be completed.
PCI DSS Compliance
Tokenization simplifies PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) compliance by eliminating the need to store sensitive card data within a merchant’s system. Since real payment details are never stored, businesses face reduced compliance requirements and lower security risks.
While encryption secures sensitive data, it still requires strong encryption key management to comply with PCI DSS. Businesses must secure encryption keys, rotate them regularly, and protect them from unauthorized access.
For example, a merchant using tokenization does not need to store credit card details, making PCI DSS compliance easier. In contrast, a merchant relying on encryption must implement strict encryption management policies to remain compliant.
Future of Payment Tokenisation
Payment tokenization is rapidly evolving and is driven by technological advancements and the increasing demand for secure, efficient transactions. Here’s a detailed look at the future landscape of payment tokenization:
Expansion Beyond Card Payments
Tokenization is set to transcend traditional card-based transactions. Its application broadens to encompass various assets, including real estate, commodities, and digital goods. This expansion facilitates the digitization and optimization of economic activities, enhancing efficiency and security across multiple sectors.
Integration with Blockchain Technology
The fusion of tokenization with blockchain is poised to revolutionize payment systems. Blockchain’s decentralized ledger offers a tamper-proof method for recording tokenized transactions, ensuring transparency and security. This integration will streamline capital markets, trade finance, and asset exchange processes.
Elimination of Manual Card Entry
Leading payment networks aim to eliminate manual card entry through tokenization by 2030. This initiative enhances security and paves the way for innovative payment forms, such as in-car commerce and Internet of Things (IoT) transactions, where devices can autonomously conduct secure payments.
Enhanced Data Privacy and Security
Tokenization minimizes the exposure of sensitive data by substituting it with non-sensitive tokens. This approach significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and fraud, fostering greater consumer trust in digital payment systems. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, tokenization will play a crucial role in safeguarding personal information.
Support for Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
As central banks explore digital currencies, tokenization will be integral in their implementation. Tokenized representations of CBDCs can facilitate secure, efficient transactions, ensuring seamless integration with existing payment infrastructures and promoting widespread adoption.
Growth in Decentralised Finance
Tokenization is a cornerstone of DeFi platforms, enabling the creation and exchange of digital assets without intermediaries. This development democratizes access to financial services, offering users greater control over their assets and fostering innovation in financial products and services.
Regulatory Developments
As tokenization becomes more prevalent, regulatory frameworks are evolving to address associated challenges. Clear guidelines are essential to ensure compliance, protect consumers, and maintain financial stability. Ongoing collaboration between industry stakeholders and regulators will shape the future of tokenization.
Conclusion
As payment technology evolves, payment tokenisation service providers lead the charge in securing digital transactions. Whether you’re an e-commerce merchant, a financial institution, or a consumer, tokenization is becoming an essential part of payment security.
With the rise of blockchain, AI-driven fraud prevention, and decentralized finance, the future of payment tokenization promises to be more secure, seamless, and efficient than ever before.
FAQ:
What is payment tokenization?
Payment is a process that substitutes sensitive payment dates, such as a credit card number, with a unique, randomly generated token to enhance security.
How does tokenization differ from encryption?
While encryption scrambles data and can be decrypted with a key, tokenization modifies data with a unique token that is not directly related to the original information.
Why is payment tokenization important?
Tokenization protects payment data from cyber threats, ensures compliance with PCI DSS regulations, and minimizes the risk of data breaches and fraud.
Where is payment tokenization used?
Tokenization is widely used in e-commerce, mobile wallets, POS systems, recurring billing, in-app purchases, and digital currencies to secure transactions.
What is the future of payment tokenization?
The future includes blockchain integration, DeFi applications, enhanced IoT payments, and seamless cross-border transactions.